Crayfish External Anatomy Shrimp and Snail Breeder

Crayfish Dissection Diagram
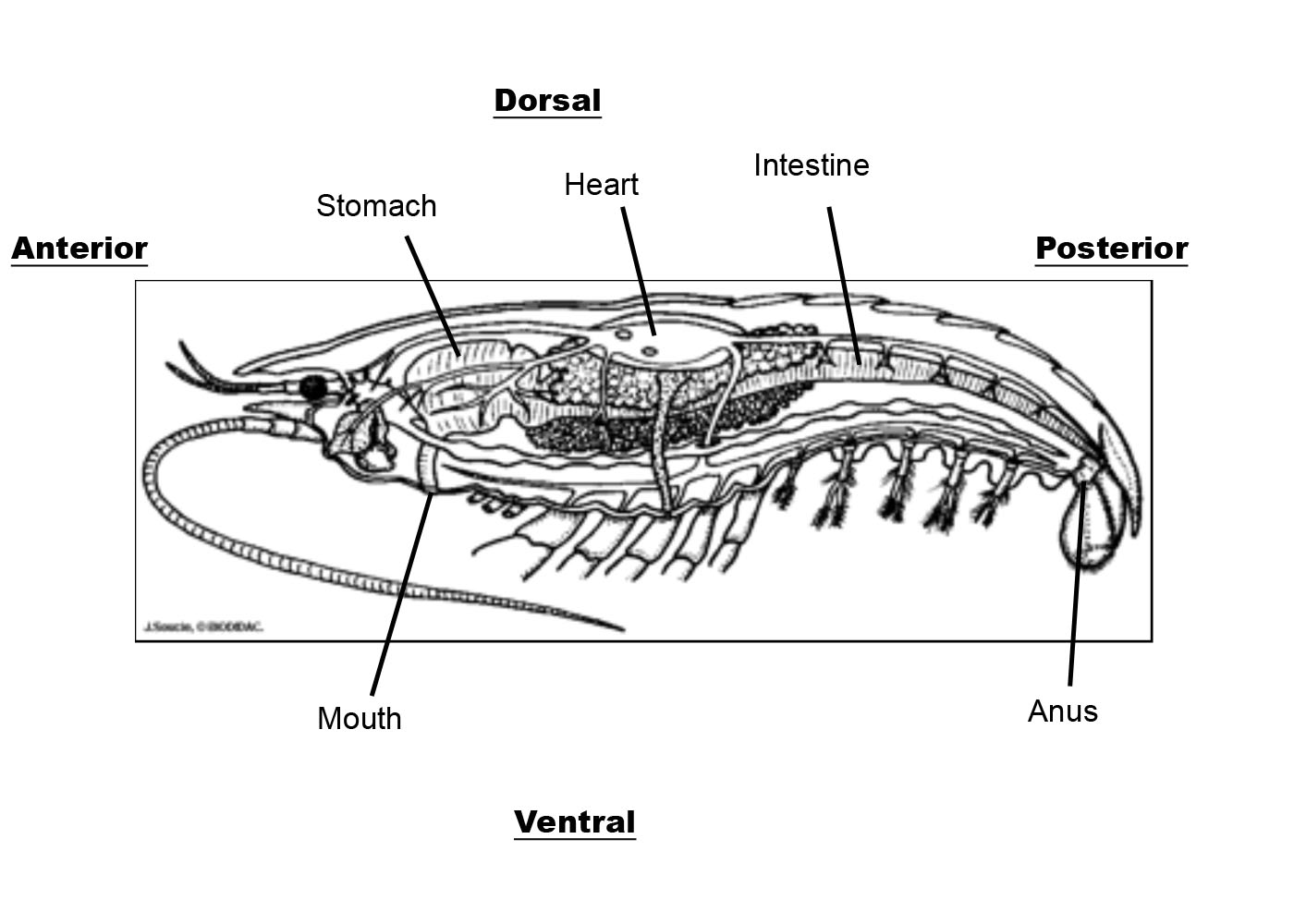
Internal anatomy of a crayfish: edible freshwater crustacean, with pincers on the two forelegs. Encephalon: site of the mental functions of a crayfish. Stomach: part of the digestive tract between the esophagus and the intestine. Heart: blood-pumping organ of the crayfish. Gonad: sex gland of a crayfish.

Crayfish External Anatomy
Crayfish are arthropods, which are the most diverse and abundant animals on earth. There are more species of arthropods than all animals combined. Arthropod characteristics: Jointed appendages - bend to move in specific directions and specialized for specific jobs

5957242b2b37e26f90f877ab6ce8c0damarinebiologyaquaponics.jpg (720×
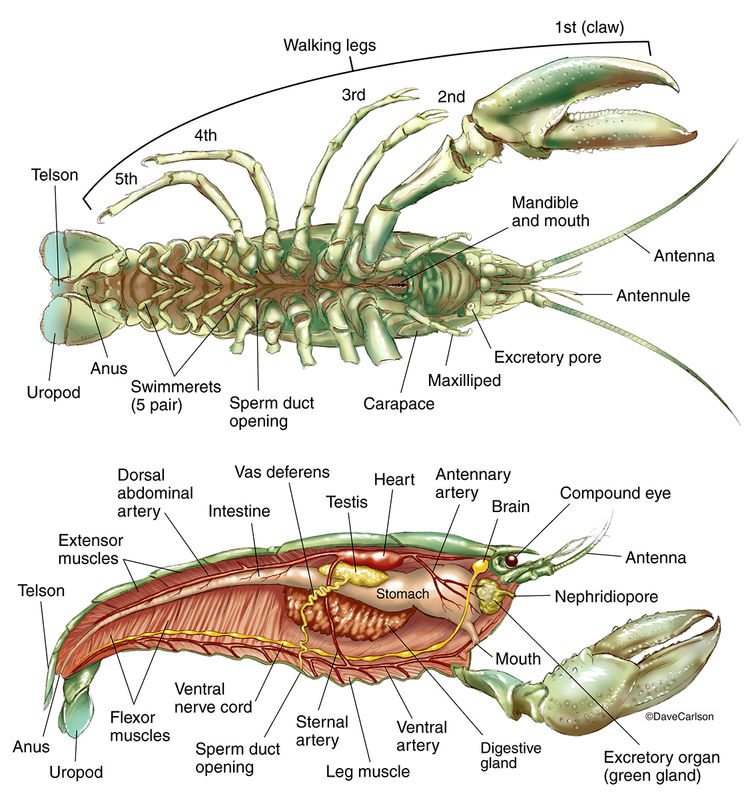
1. The cephalothorax The cephalothorax (cephalic+ thoracic) consists of the cephalic (or head) region and the thoracic (or chest) region. In its turn, the chest also consists of 3 segments that can be seen only from the ventral side of the crayfish where each segment contains a pair of appendages that are called walking legs.

Lesson 5 The Crayfish (Crustacean) C.S.W.D
Social Studies. World Languages. This video details the external anatomy of a crayfish and compares it to other arthropods.
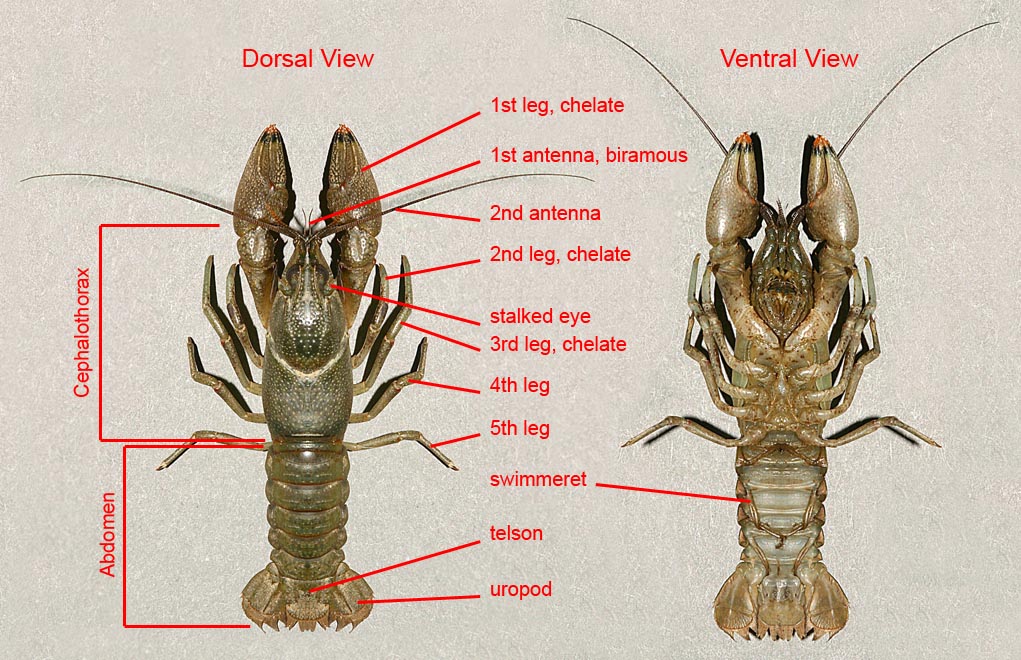
Labeled Diagram Of A Crayfish
Arachnids breathe via book lungs. More information on arachnids will follow in a subsequent lab. Subphylum Crustacea ( crusta = crust, rind) includes crayfish and lobsters, crabs, pillbugs, and several other groups. They have gills, thus terrestrial pillbugs need to maintain a 100% humidity environment around their gills to be able to "breathe."

Crayfish Diagrams 101 Diagrams
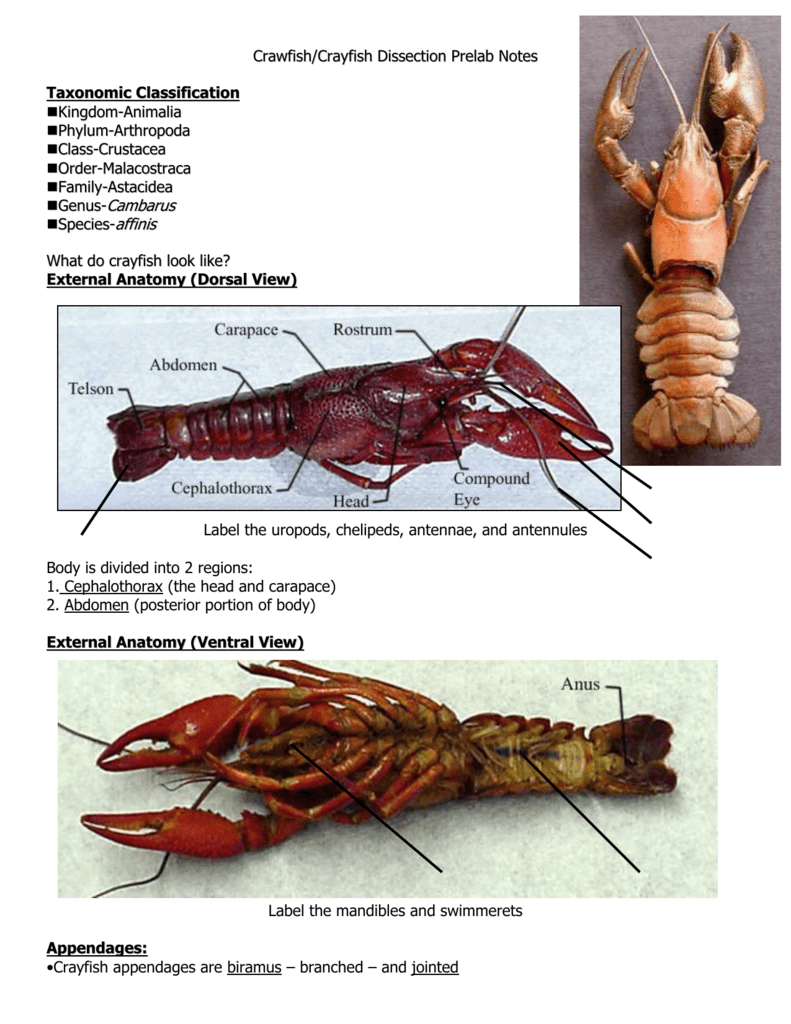
External Anatomy Step 1 Place the preserved crayfish in a dissecting tray. Step 2 Note that the body of the crayfish is divided into three parts: the head, the cephalothorax, and the abdomen. Step 3 Head - Identify the compound eyes on the rostrum portion of the head. Step 4
Zoology Carlson Stock Art
Objectives: Students will be able to identify types of crustaceans and provide examples. Students will be able to describe the basic biology of aquacultured crustaceans. Students will be able to identify key anatomical features of common crustacean species.

Crayfish Internal Anatomy Shrimp and Snail Breeder
In this Biology lab, we will take a close look at the external and internal anatomy of a freshwater aquatic invertebrate—the crayfish. As we study the anatom.

crayfish. arthropods arthropods activity Crayfish, Biology, Arthropods
Most adult crayfish are about 7.5 cm (3 inches) long. Among the smallest is the 2.5-cm-long Cambarellus diminutus of the southeastern United States.Among the largest is Astacopsis gouldi of Tasmania, which may reach 40 cm in length and weigh about 3.5 kg (8 pounds).. Crayfish, common in streams and lakes, often conceal themselves under rocks or logs.

Crayfish Internal Anatomy Shrimp and Snail Breeder
The Anatomy of a Crayfish. Let's take a closer look at the anatomy of a crayfish. These creatures have a segmented body that is divided into two main regions: the cephalothorax and the abdomen. The cephalothorax contains the head, which includes the eyes, antennae, and mouthparts, as well as the thorax, which houses the walking legs and small.

Crayfish Dissection C1W7 Classical Conversations Cycle 1 Classical
The purpose of this lab activity is to help you learn the anatomy of a crayfish and give you a better understanding of the anatomy of invertebrate animals in general. After completing this dissection, you should be able to: Correctly identify the locations involved in the dissection procedures, and

crayfish anatomy diagram
1. Place the crayfish with its dorsal (top) side up in a dissection tray. Use the diagram below to locate the cephalothorax and the abdomen. The carapace, a shield of chitin, covers the dorsal surface of the cephalothorax.
Crawdads in NC Lucky Sci
The Body. The body of the crayfish consists of a fused head and thorax: the cephalothorax. The cephalothorax is covered by a thick armor called a carapace. Extending from the carapace is a pointy structure called the rostrum. Locate the cephalothorax and rostrum. The abdomen of the crayfish is segmented and flexible.

Labeled Crayfish Diagram
Day 1 I. Abdomen - Ventral View (Day 1) top Place the crayfish supine (ventral surface up) on the dissecting tray and DRAW the following: Telson (What is the telson's function?) Uropod (Describe the location of the Uropod to the telson. How do the add to the telson's function?)

Dorsal view of generalized male crayfish (Redrawn from Hobbs 1976
Answers EnchantedLearning.com Label Crayfish External Anatomy Crayfish Printout More on Crustaceans Read the definitions below, then label the crayfish diagram. Abdomen - The abdomen is the segmented tail area. The swimmerets, telson, and uropods are attached to the abdomen. Carapace - The protective shell (exoskeleton) of the cephalothorax.
Internal Anatomy Crayfish Anatomy Book
Abdomen The abdomen is flexible and the segmentation is visible here. The appendages of the crayfish attach to both the cephalothorax and the abdomen. The appendages that attach to the thorax are called WALKING LEGS and you can see how they are jointed in the figure below.