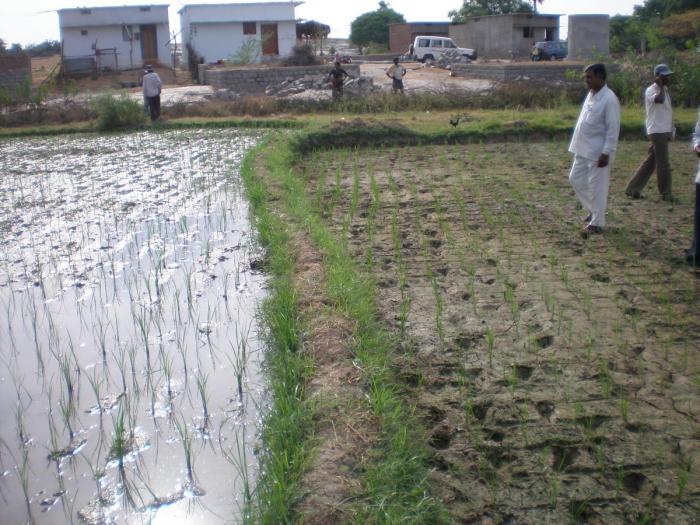
Wetting and Drying Process in Rice System తడిపొడి విధానంతో

(PDF) Alternate wetting and drying in irrigated rice Implementation guidance for policymakers
CH4 emissions were observed under alternate wetting and drying than continuous flood-ing [20,21]. Islam et al. [20] conclude that GHG emission-reducing technology (e.g., urea deep placement or UDP) combined with a water-saving management strategy like AWD compared to rice production under continuous flooding conditions is effective.

Alternate Wetting and Drying Isbell Farms
Alternate wetting and drying ( AWD) is a water management technique, practiced to cultivate irrigated lowland rice with much less water than the usual system of maintaining continuous standing water in the crop field. It is a method of controlled and intermittent irrigation.

Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) Climate Smart Agriculture
Alternate wetting and drying (AWD) is a simple and inexpensive way of reducing water consumption in rice production by 30%, thus, enabling farmers to cut down on production cost without yield penalty. AWD entails periodic draining of the field to a certain threshold, usually 15 cm below the soil surface, and re-flooding..

Infographic Alternate wetting and drying in irrigated rice
Alternate wetting and drying (AWD) has been recognized as a water-saving technology in rice production systems; however, pre- and post-flowering AWD could induce changes in yield, quality and aroma biosynthesis in fragrant rice. In the present study, two fragrant rice cultivars (Guixiangzhan and Nongxiang-18) were subjected to AWD.

Alternate Wetting and drying irrigation (AWD) showing (a)Breakthrough... Download Scientific
The alternate wetting and drying (AWD) as water-saving technology aligns with the good agricultural practices (GAP) principles, particularly in the environmental management of water conservation. Thus, GAP adopters as farmer groups are seen as viable AWD adopters in the initial stages of scaling out the adoption in Thailand. However, the understanding of integrating AWD as water-saving.

Alternate wetting and drying before and after 25 and 50 cycles. Download Scientific Diagram
Alternate wetting and drying (AWD) irrigation is panacea for water scarcity glitches (Pourgholam-Amiji et al., 2020). Keywords: Frequent, harmful, highest, insect pest infestation,.

alternate wetting and drying The Rice Stuff
Alternate wetting and drying (AWD) is a water-saving and eco-friendly option. • AWD requires 25-70 % less water than conventional system without yield reduction. • AWD reduces GHGs emission and restrict As and Hg accumulation in rice grains. Abstract

Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) Irrigation YouTube
Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) is a water-saving technology that farmers can apply to reduce their irrigation water consumption in rice fields without decreasing its yield. In AWD, irrigation water is applied a few days after the disappearance of the ponded water. Hence, the field gets alternately flooded and non-flooded.
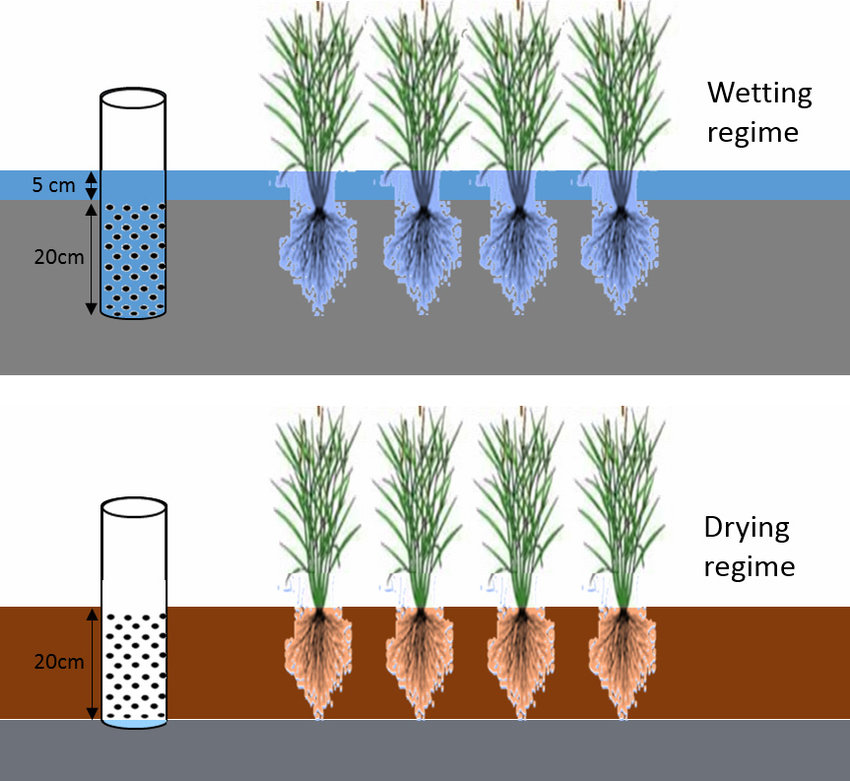
Wetting and Drying Process in Rice System తడిపొడి విధానంతో
Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) is a well-known low-cost water-saving and climate change adaptation and mitigation technique for irrigated rice. However, its adoption rate has been low despite the decade of dissemination in Asia, especially in the Philippines. Using cross-sectional farm-level survey data, this study empirically explored factors shaping AWD adoption in a gravity surface.

(PDF) Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) irrigation A smart water saving technology for rice
Alternate wetting and drying (AWD) is a simple and inexpensive way of reducing water consumption in rice production by 30%, thus, enabling farmers to cut down on production costs without yield penalty. AWD entails periodic draining of the field to a certain threshold, usually 15 cm below the soil surface, and re-flooding.
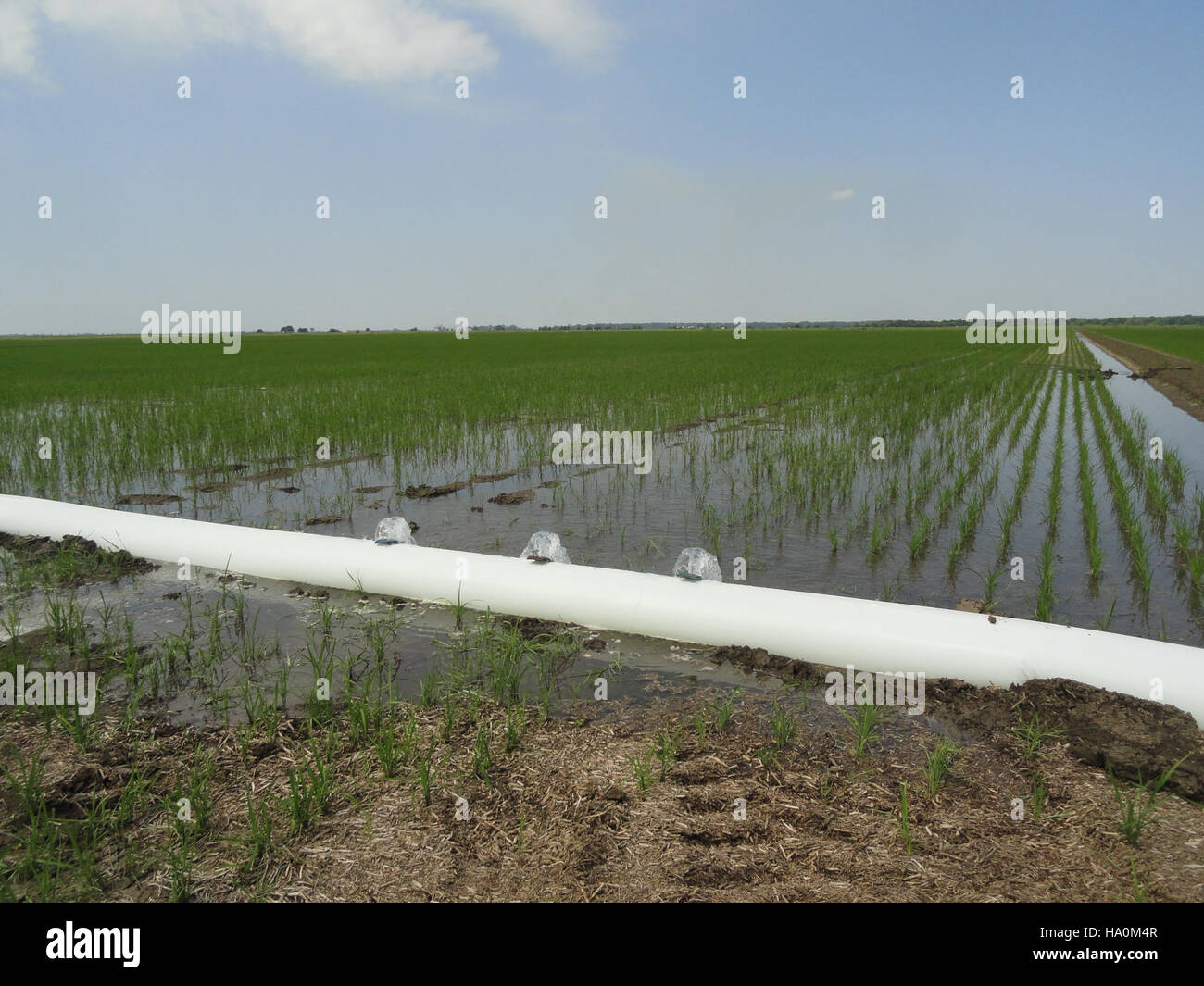

usdagov 19587335711 Poly pipe and alternate wetting and drying Stock Photo Alamy
Alternate wetting and drying (AWD) is an agriculture technique that can make rice cultivation more resilient to water scarcity caused by climate change and even help reduce methane emissions linked to rice production. AWD techniques alternate flooding and draining of fields throughout the process.
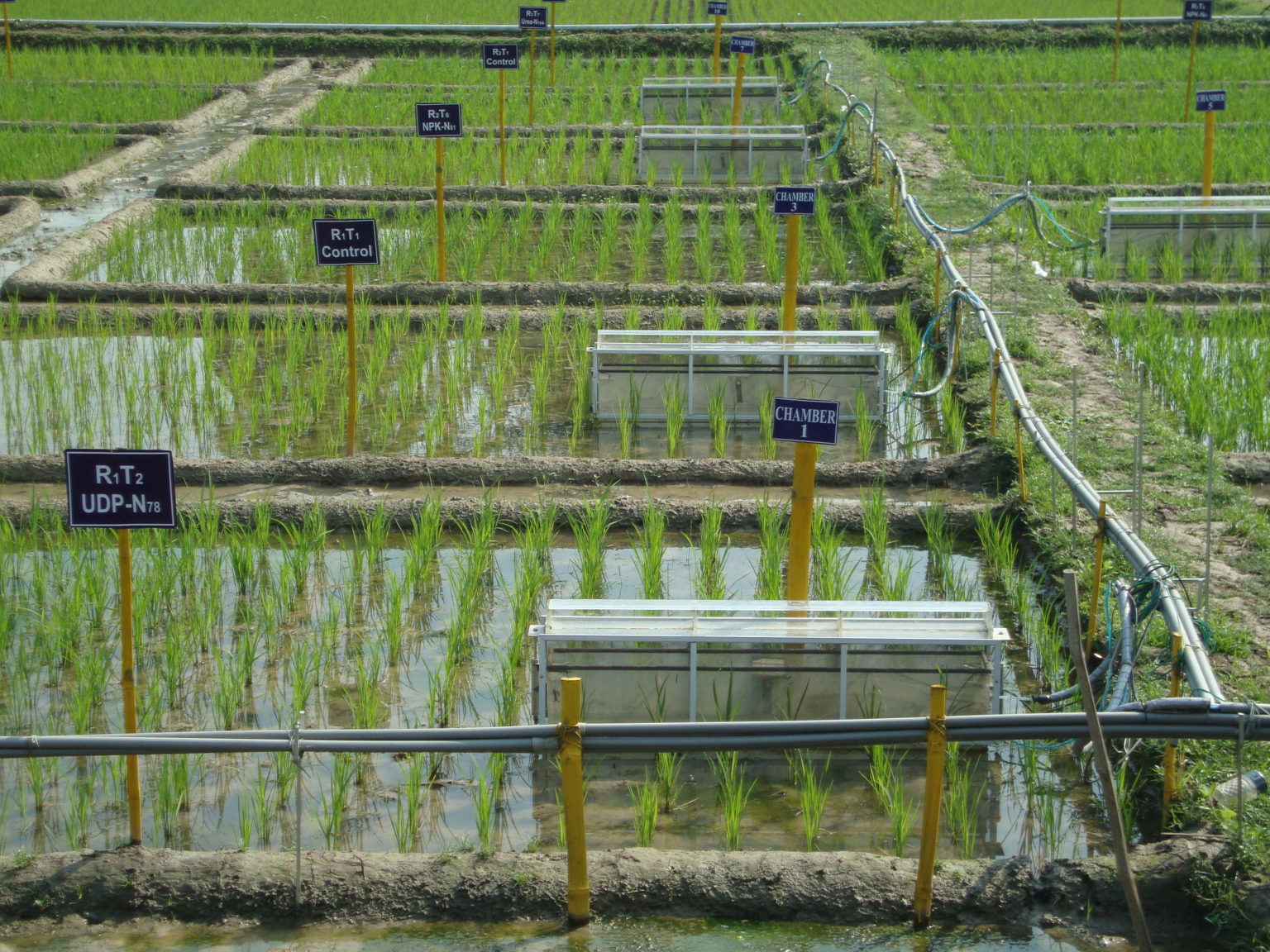

Mitigating GHG Emissions from Rice Fields through Alternate Wetting and Drying Irrigation IFDC
75 of The Top 100 Retailers Can Be Found on eBay. Find Great Deals from the Top Retailers. eBay Is Here For You with Money Back Guarantee and Easy Return. Get Your Drying Today!

1704 Alternate wetting and drying and the System of Rice Intensific…
The conventional practice of alternate wetting and drying (AWD) irrigation technique that typically starts at 21 days after transplanting (DAT) can hardly reduce this emission because the soil become methanogenic before the onset of AWD treatment.

How to Make Alternate Wetting and Drying YouTube
Alternate wetting and drying (AWD) is widely regarded as a water-saving irrigation technology capable of contributing to sustainable water-use. Existing literature lacks rigorous quantitative analysis of the determinants and effects of AWD adoption. In contrast, applying logit, propensity score matching and multiple regression models.

ClimateSmart Land Use Insight Brief No. 2 Alternate wetting and drying for climate change
Alternate wetting and drying is a promising, profitable, and ecofriendly technology for rice cultivation across the globe. The efforts are underway to commercialize it in water-scarce areas. The adoption of mild/safe-AWD reduces the total water inputs as compared to CF while maintaining or increasing the yield. However, severe-AWD.

Alternate wetting and drying in rice systems 10 Innovations YouTube
Sustainable Development Goals Climate action and life on land Alternate wetting and drying (AWD) is a water-saving technology that lowland (paddy) rice farmers can apply to reduce their water use in irrigated fields. In AWD, irrigation water is applied to flood the field a certain number of days after the disappearance of ponded water.