Lung Anatomy & Function Lung Nodule, Lung Disease and Lung Infection
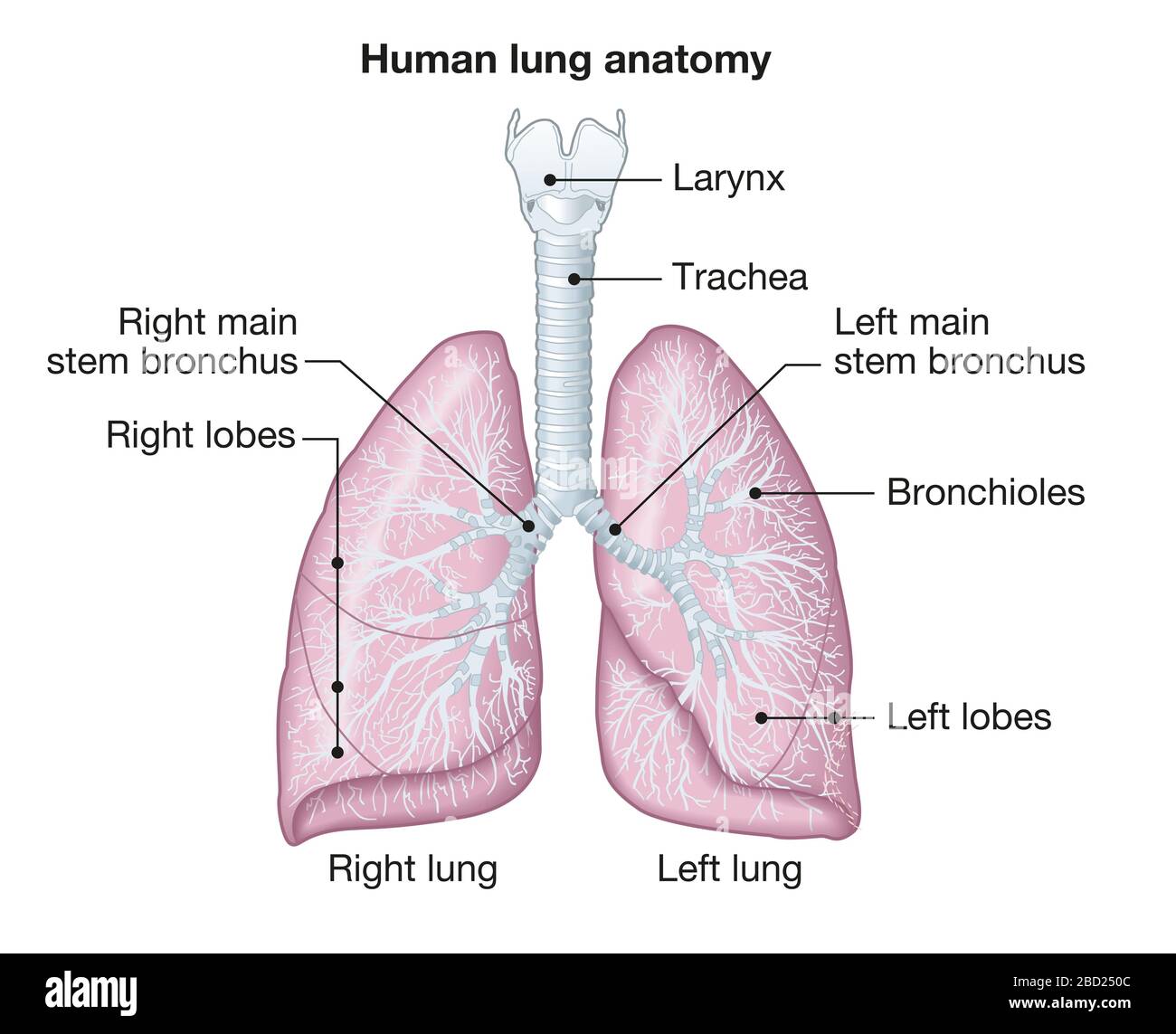
Lungs anatomy hires stock photography and images Alamy
The respiratory system consists of two components, the conducting portion, and the respiratory portion. The conducting portion brings the air from outside to the site of the respiration.. The lung is identified, dissected en-block, weighed, and labeled. Later the lung is perfused with 10% formalin through the trachea to the physiological.
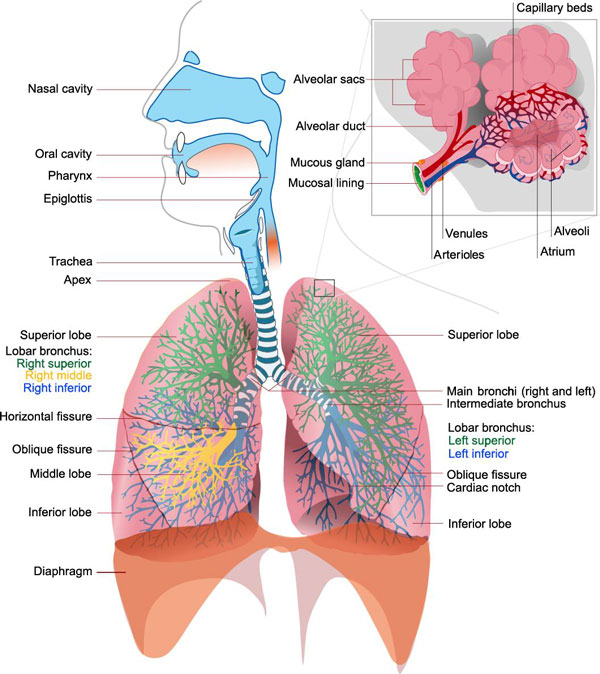
lungs
The purpose of the lung is to provide oxygen to the blood. The respiratory system divides into airways and lung parenchyma. The airways consist of the bronchus, which bifurcates off the trachea and divides into bronchioles and then further into alveoli. The parenchyma is responsible for gas exchange and includes the alveoli, alveolar ducts, and bronchioles. Lungs have a spongy texture and have.
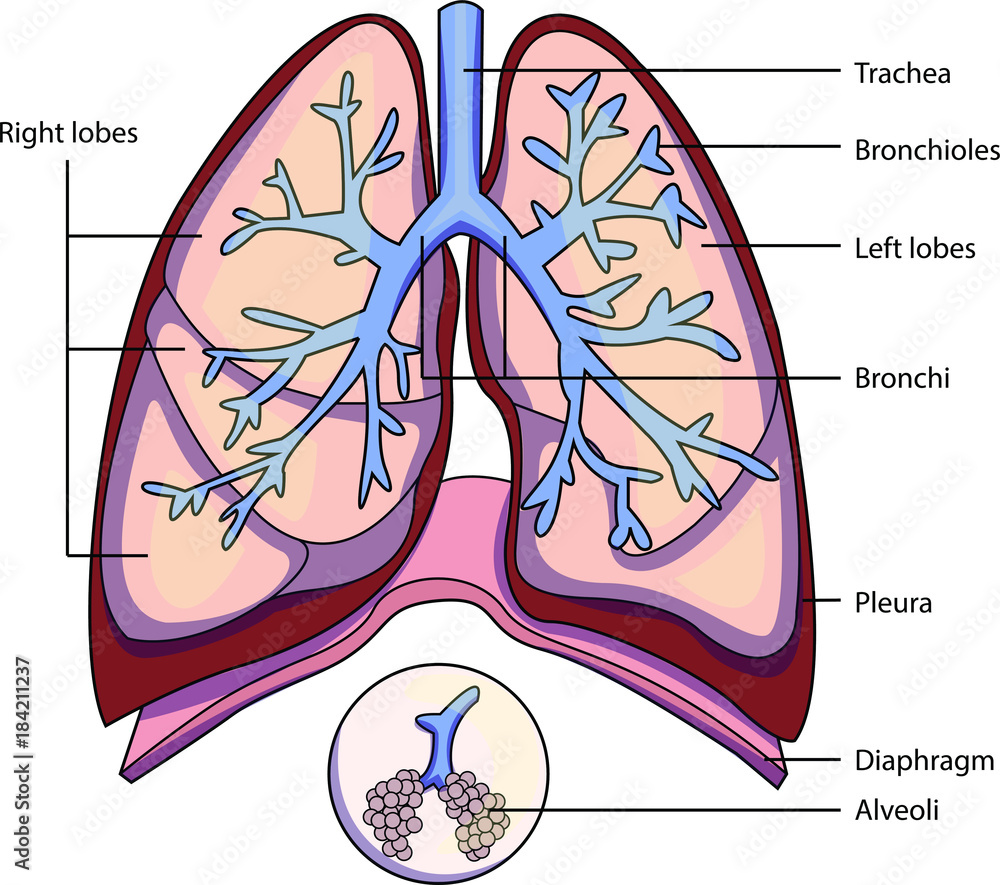
The structure of a lung with labeled parts. Biology vector illustration
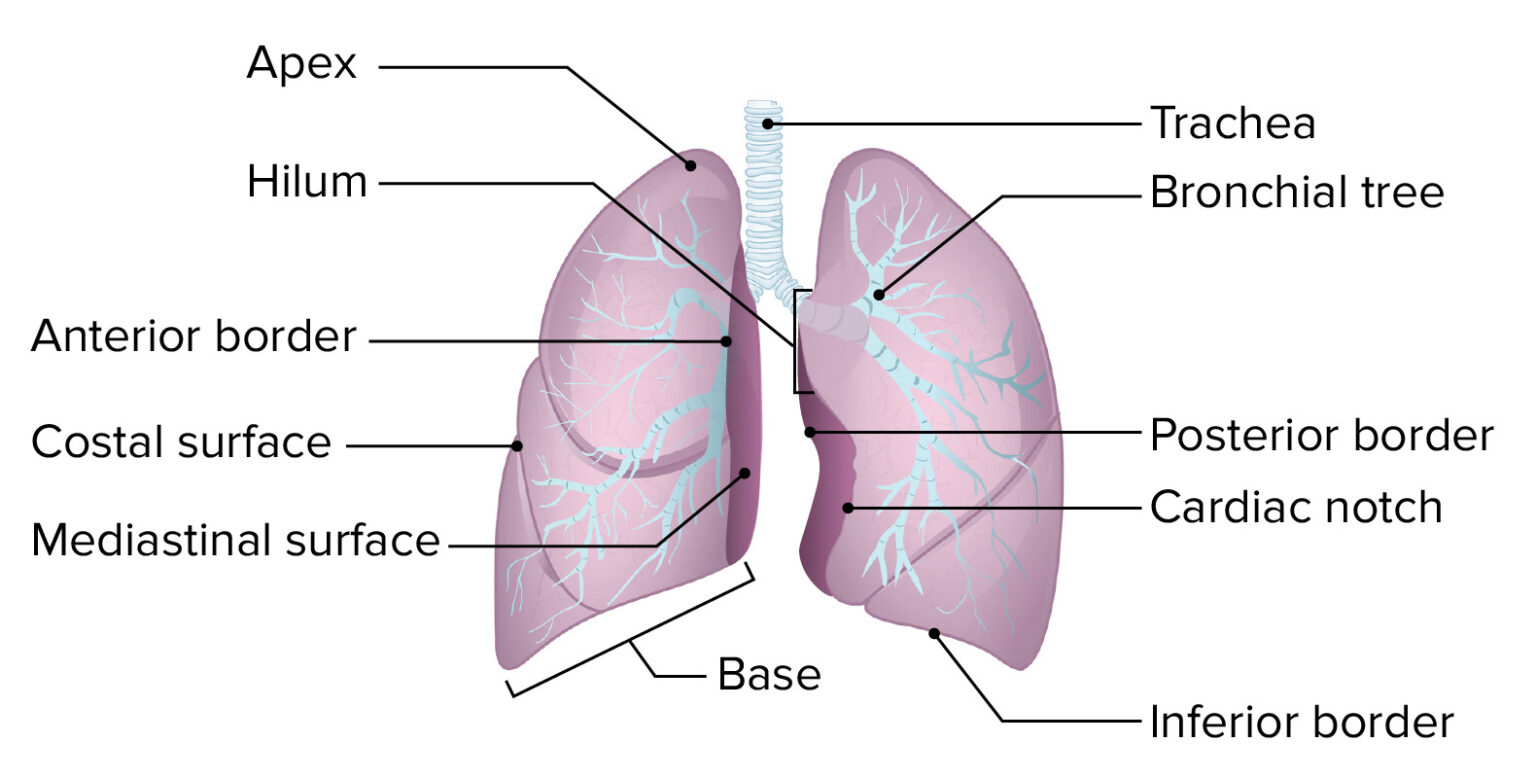
Lung Structure The lungs are roughly cone shaped, with an apex, base, three surfaces and three borders. The left lung is slightly smaller than the right - this is due to the presence of the heart. Each lung consists of: Apex - The blunt superior end of the lung. It projects upwards, above the level of the 1st rib and into the floor of the neck.

Sections of the Lungs Seattle Cancer Care Alliance
Total Lung Capacity (TLC) and Lung Compliance. TLC refers to the maximum volume of air the lungs of an adult person can hold. It is the sum of the air released by the lung after a maximum exhalation (vital capacity or VC) and the volume of air left behind within the lungs after a deepest exhalation (residual volume or RV) [46].The TLC of human lungs is 6 liters [47].
How do we breathe? (Lungs and Pleura) Interactive Biology, with
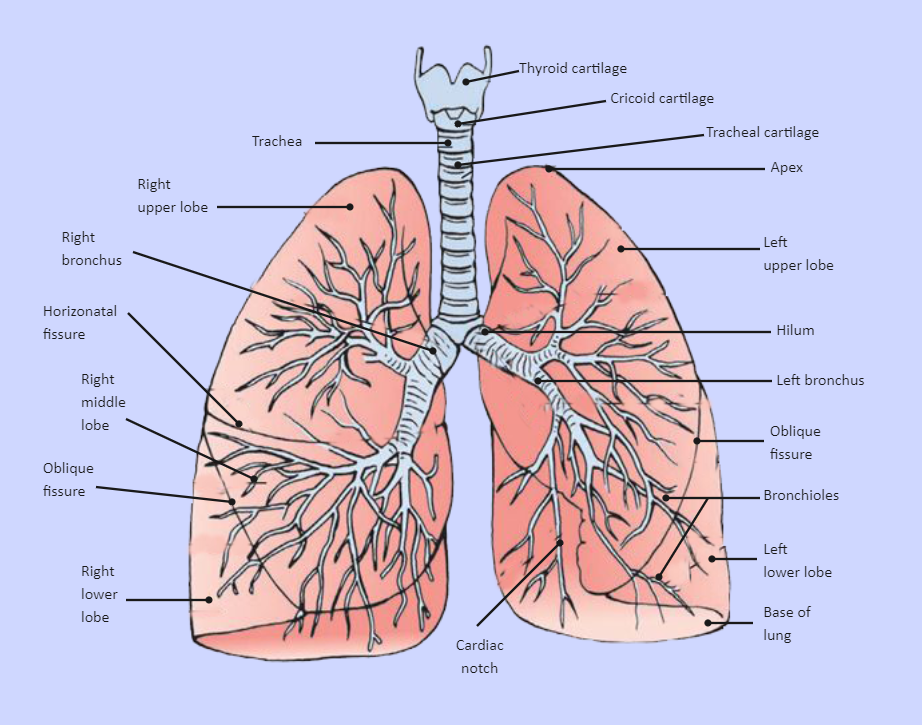
Larynx: The larynx is essential to human speech. Lower respiratory tract: Composed of the trachea, the lungs, and all segments of the bronchial tree (including the alveoli), the organs of the.

Lung Anatomy & Function Lung Nodule, Lung Disease and Lung Infection
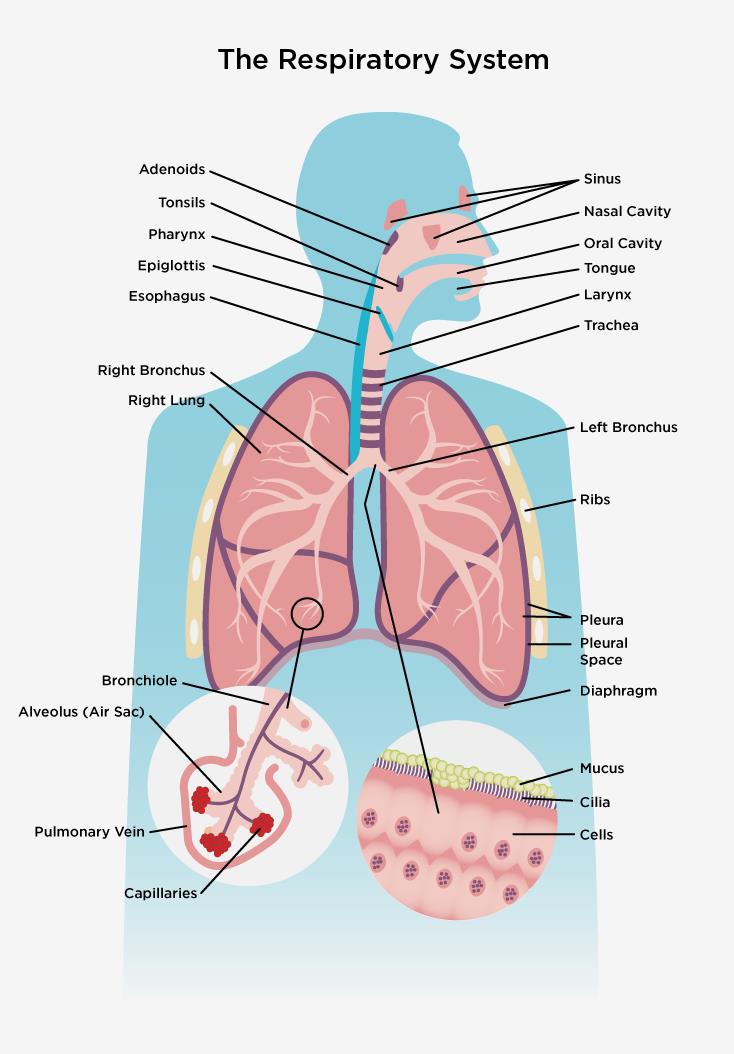
The respiratory system, also called the pulmonary system, consists of several organs that function as a whole to oxygenate the body through the process of respiration (breathing).
Respiratory system Canadian Lung Association
The lungs are the center of the respiratory (breathing) system. Every cell of the body needs oxygen to stay alive and healthy. Your body also needs to get rid of carbon dioxide. This gas is a.
Lungs Anatomy Concise Medical Knowledge
Overview A step-by-step explanation of how your lungs work. What are your lungs? Your lungs make up a large part of your respiratory system, which is the network of organs and tissues that allow you to breathe. You have two lungs, one on each side of your chest, which is also called the thorax.

The lungs Lung cancer Macmillan Cancer Support
Lungs Diagram in Human Body Humans have a right and a left lung positioned in the chest cavity. Jointly, the lungs inhabit most of the intrathoracic space. Lungs are responsible for adding oxygen and removing carbon dioxide from the blood, thus serving as a gas-exchanging structure for respiration.

Lungs Definition, Location, Anatomy, Function, Diagram, Diseases
Publication date: Aug 5, 2010 | Last update: Oct 5, 2022 https://doi.org/10.37019/e-anatomy/93511 ISSN 2534-5079 This e-Anatomy module presents an illustrated anatomy of the lungs, trachea, bronchi, pleural cavity and pulmonary vessels.

Overview of the Respiratory System Function and Structure Thoracic Key
Respiratory system diagram The respiratory system How we breathe Respiratory conditions Summary The respiratory system allows air to reach the lungs, from which oxygen enters the blood.
The lungs Macmillan Cancer Support
Lungs are a pair of respiratory organs situated in a thoracic cavity. Right and left lung are separated by the mediastinum. Texture -- Spongy Color - Young - brown Adults -- mottled black due to deposition of carbon particles Weight- Right lung - 600 gms Left lung - 550 gms THORACIC CAVITY SHAPE - Conical Apex (apex pulmonis) Base

Respiratory System Anatomy
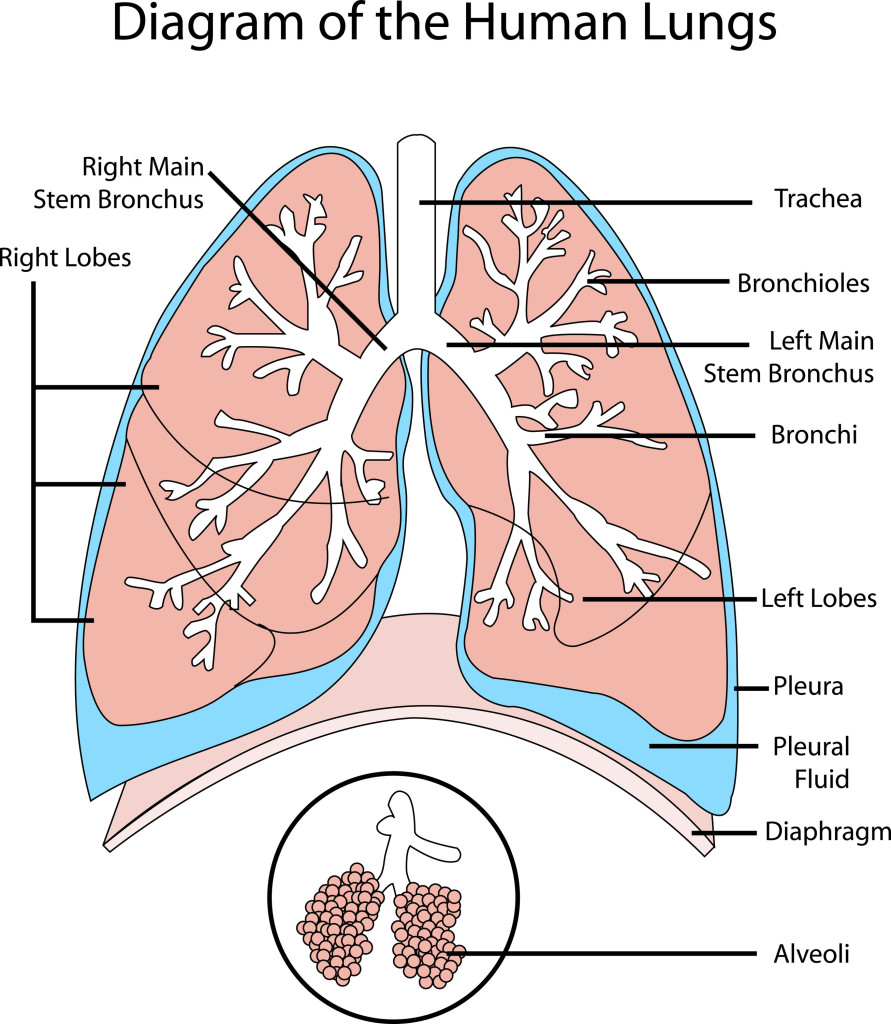
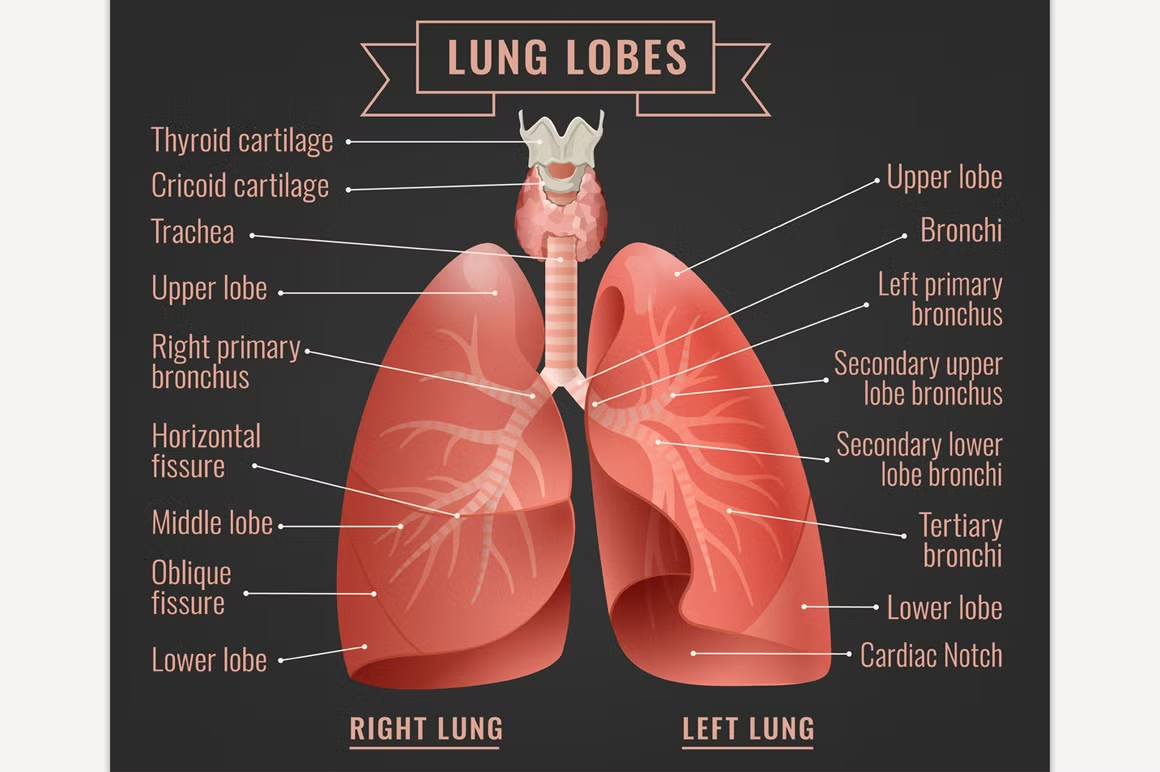
Given below is a labeled diagram of the human lungs followed by a brief account of the different parts of the lungs and their functions. Each lung is enclosed inside a sac called pleura, which is a double-membrane structure formed by a smooth membrane called serous membrane.
Lung Diagram Labeled EdrawMax Template
The lungs are respiratory organs - we use them to breathe. We breathe in order to get oxygen (O 2) and to get rid of carbon dioxide (CO 2 ). We breathe in through the nose or mouth. The air then goes through the larynx and the trachea (also called the windpipe) and into the lungs. We breathe by using the diaphragm, a muscular membrane under.

Lung Structure BioNinja
The diaphragm is the flat, dome-shaped muscle located at the base of the lungs and thoracic cavity. The lungs are enclosed by the pleurae, which are attached to the mediastinum. The right lung is shorter and wider than the left lung, and the left lung occupies a smaller volume than the right.
Human lungs infographic Education Illustrations Creative Market
Anatomy Organs Anatomy of the Lungs A spongy organ that moves oxygen through the bloodstream By Colleen Travers Updated on August 16, 2023 Medically reviewed by Scott Sundick, MD Table of Contents Anatomy Function Associated Conditions Tests