Related image Anatomy of the tongue, Anatomy, Human tongue

Sulcus lateralis Ars Neurochirurgica
Der Sulcus lateralis linguae (lat. für „seitliche Zungenfurche") ist ein zwischen dem Zungenboden und Unterkieferknochen verlaufender dreiseitiger Spalt bzw. Kanal. Er wird oben durch den Musculus hyoglossus, unten durch den Musculus mylohyoideus und seitlich durch den Unterkiefer begrenzt.
PPT Trávicí systém (apparatus digestorius) PowerPoint Presentation ID4148661
Surgical Anatomy of the Tongue Mahmoud F. Sakr Chapter First Online: 24 August 2022 609 Accesses Abstract The tongue (Latin, lingua; Greek, glos sa) is a unique organ located in the oral cavity. It has importance in the digestive system and is the primary organ of taste in the gustatory system.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0)/images/anatomy_term/terminal-sulcus-of-tongue/BQMiolUVECN7aPO1fd5Shg_Sulcus_terminalis_02.png)
Terminal sulcus of tongue (Sulcus terminalis linguae) Kenhub
The lingual sulcus release technique described here finds its utility in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue tumours in patients with limited mouth opening (grade I/II trismus), in which there is involvement of the ventral surface of the tongue with extension to the floor of the mouth (Fig. 1).Download : Download high-res image (315KB) Download : Download full-size image

The inner cortex and lingual periosteum of the mandible and floor of... Download Scientific
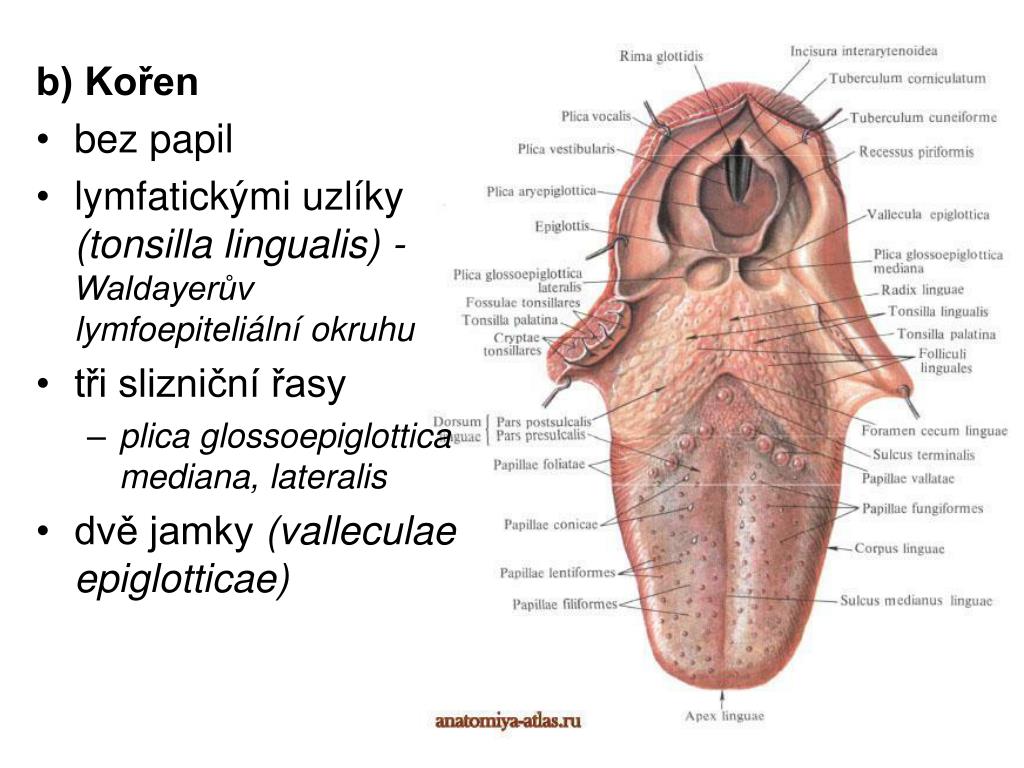
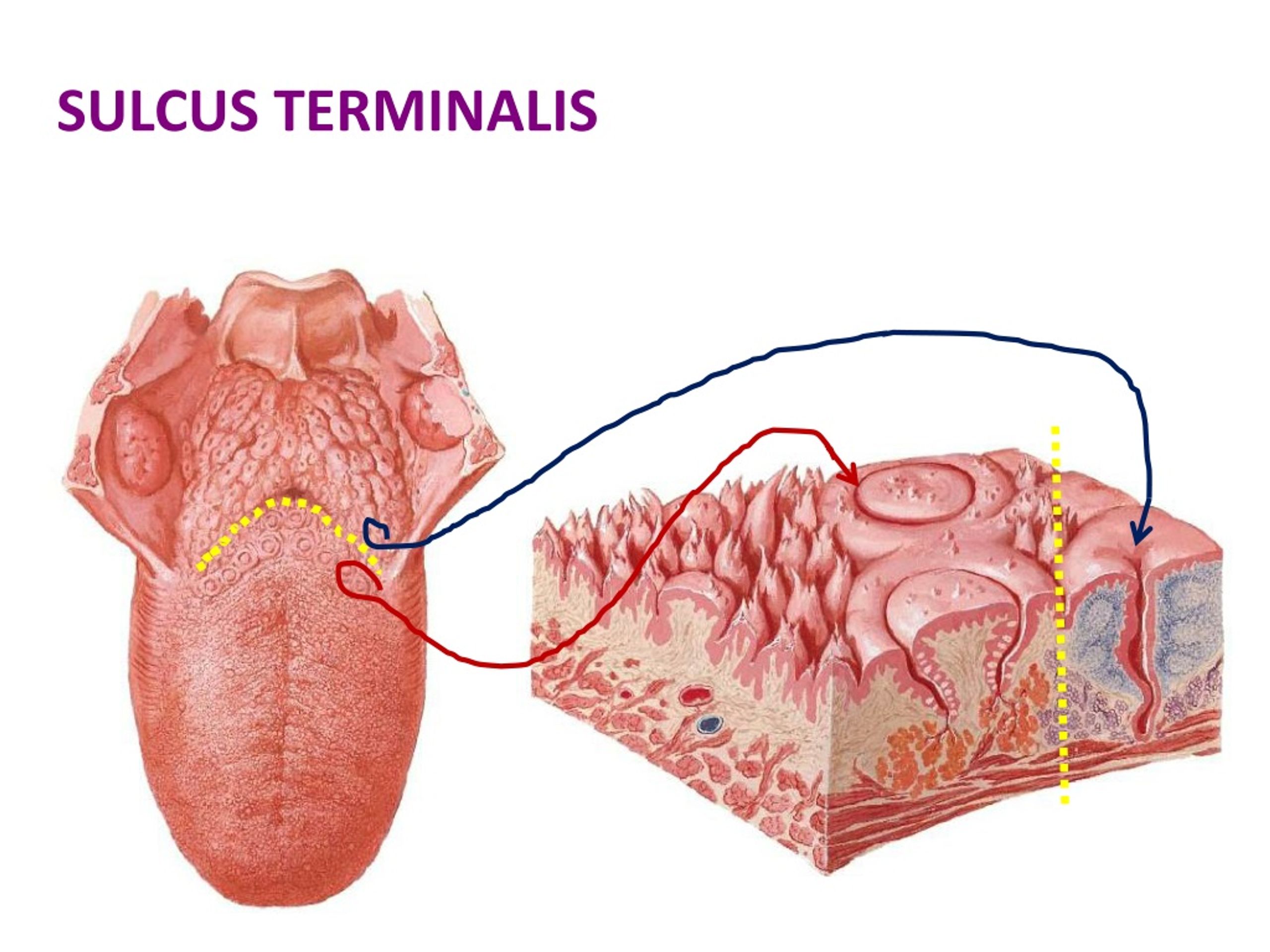
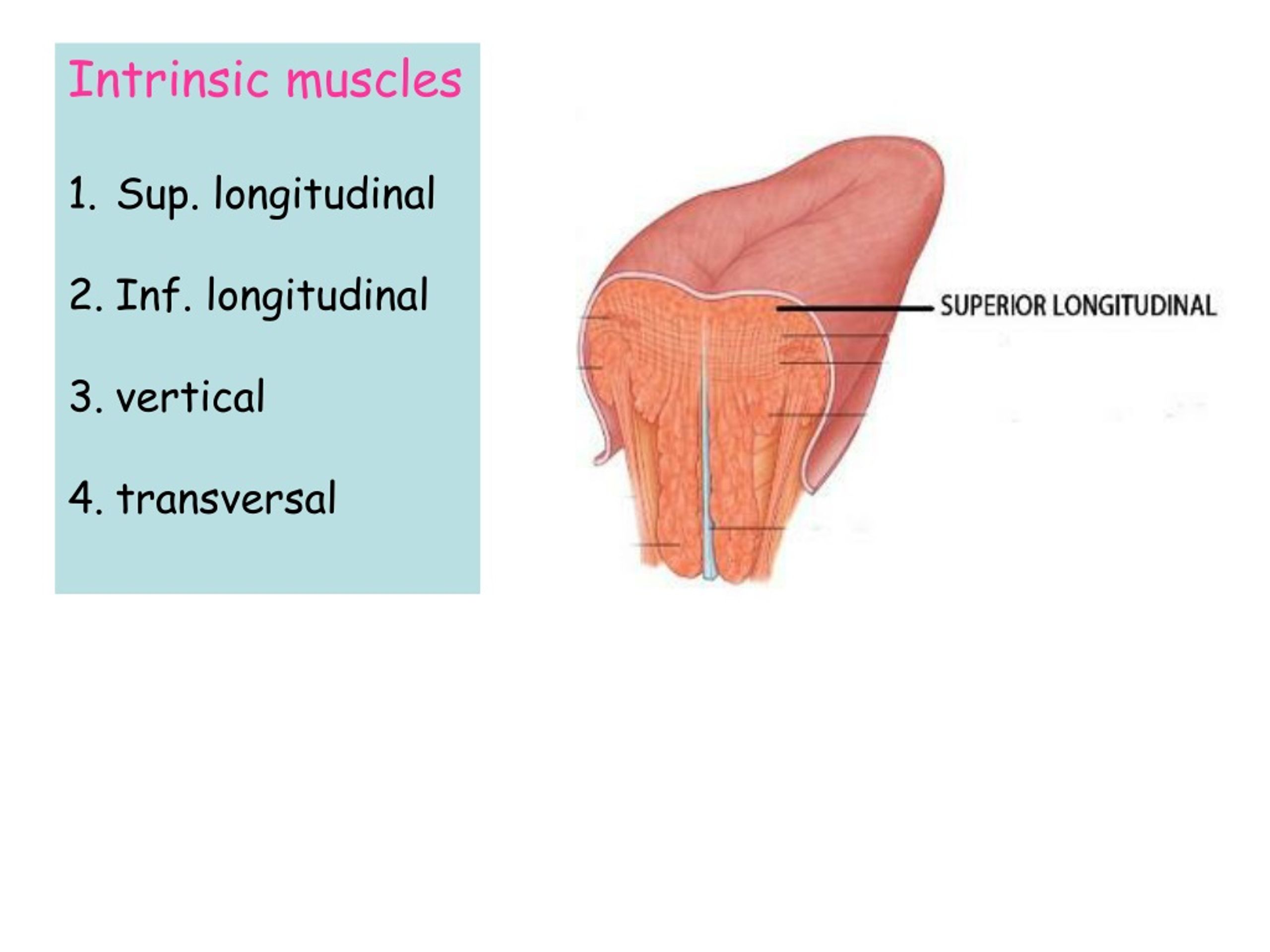
Dr. Altdorfer: The tongue - Anatomy, histology, innervation Sulcus terminalis Foramen cecum Root Follicular part Dorsum linguae Papillar part Apex linguae. Intrinsic muscles • Sup. longitudinal • Inf. longitudinal • vertical • transversal. SUBLINGUAL REGION • frenulumlinguae • deeplingualvein • sublingual fold • sublingualcaruncula (papilla)

theanatomyofthetongue Google Search Anatomy Head, Anatomy Bones, Body Anatomy, Anatomy Of
The Sylvian fissure, also known as the lateral sulcus or fissure, begins near the basal forebrain and extends to the lateral surface of the brain separating the frontal and parietal lobes superiorly from the temporal lobe inferiorly 3.The insula is located immediately deep to the Sylvian fissure.. Gross anatomy. The Sylvian fissure can be divided into superficial and deep portions 3,4.

Human Anatomy Scientific Illustrations Nervus Lingualis HighRes Vector Graphic Getty Images
The torus linguae, a raised portion of the tongue caudal to the lingual fissure. The buccal papillae, are conical papillae lining the inside of the cheeks. The surface of the tongue is covered in papillae, including the large round vallate papillae (with a moat encircling each one) near the root of the tongue.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/arteria-dorsalis-linguae/brdasWhvZZ9Coh8ZOGsE0Q_A._dorsalis_linguae_01.png)
Tongue Nerve and blood supply (lingual artery) Kenhub
Walls of Sulcus lateralis linguae-M. Mylohyoideus (lateral)-M. Hyoglossus (medial) Alveolo-lingual mucosa (superior) Sets found in the same folder. Anatomy Module#3 Part#1. 221 terms. anandam288. ANATOMY PART#2. 238 terms. anandam288. ANATOMY part#3. 179 terms. anandam288. Cranial nerves Midterm exam. 95 terms. anandam288. Other sets by this.

Tongue muscles, Anatomy, Anatomy of the tongue
hard and soft palate mucosa overlying sublingual and submandibular glands + tongue. buccal mucosa ROOF Palate ORAL CAVITY PROPER LATERAL WALL Bucca TONGUE Sulcus paralingualis FLOOR Oral diaphragm
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/arteria-lingualis-2/7URLOLjzx5gRwRvXyrUIw_A._lingualis_m01.png)
Tongue Nerve and blood supply (lingual artery) Kenhub
In 33.3%, one of the terminal branches of the mylohyoid nerve after perforating the homonymous muscle, anastomoses with the lingual nerve in the lateral sulcus of the tongue (Sulcus lateralis linguae) achieving, in the author's opinion, the "mylohyoid or sublingual curl".
PPT Dr. Altdorfer The tongue Anatomy, histology, innervation PowerPoint Presentation ID
The lateral lingual groove (or sulcus) is a V-shaped space located between the hyoglossus and mylohyoid muscles. Figure 1. Lateral lingual groove Subscribe now to continue reading Join hundreds of successful students who use Meddists to ace their exams. Gain access to all of the material and topics, custom-made just for you. Continue

Reference points used for measurements on the casts (A) lingual sulcus... Download Scientific
SULCUS LATERALIS LINGUAE SULCUS MEDIALIS LINGUAE Határai: medialis: m. hyoglossus lateralis: m. mylohyoideus felső: paralingualis nyálkahártya Tartalma: n. lingualis d. submandibularis n. hypoglossus + * v. comitans cum nervo hypoglosso.
TongueGross Anatomy & Applied Aspects. Dr.N.Mugunthan.M.S
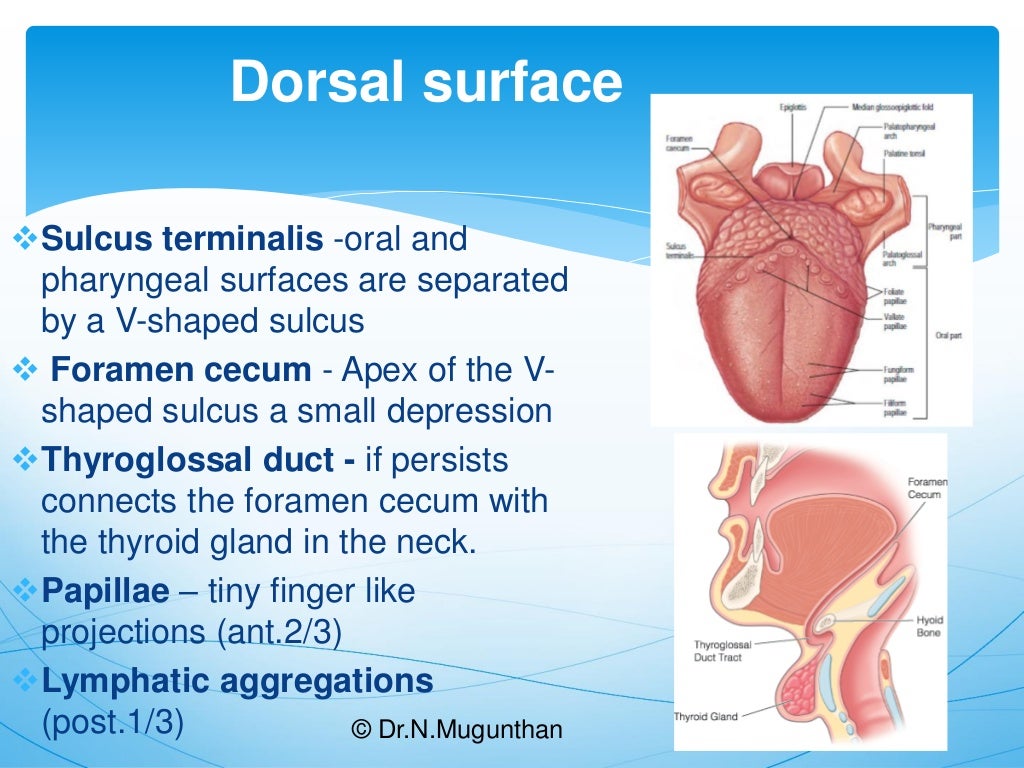
Definition. The median sulcus divides the dorsum of the tongue into symmetrical halves; this sulcus ends behind, about 2.5 cm. from the root of the tongue, in a depression, the foramen caecum, from which a shallow groove, the sulcus terminalis, runs lateralward and forward on either side to the margin of the tongue.

Pin by Will Housell on Lickilicky Throat anatomy, Tongue, Anatomy
Definition Der Sulcus lateralis linguae ist ein anatomischer Spaltraum, der sich zwischen dem Musculus mylohyoideus und dem Musculus hyoglossus befindet. Anatomie Der Sulcus lateralis linguae lässt sich als Verlängerung des Recessus sublingualis lateralis unterhalb der Mundschleimhaut verstehen. In ihm verlaufen folgende Strukturen:

Dorsal Surface Of Tongue , Png Download Tongue Diagram Simple, Transparent Png , Transparent
The sulcus lateralis linguae (Latin for "lateral tongue furrow") is a three-sided gap or canal running between the base of the tongue and the lower jaw bone. It is bounded above by the hyoglossus muscle, below by the mylohyoid muscle and laterally by the lower jaw.. The structures running in it are from top to bottom: Nervus lingualis; Sublingual vein (variable)
PPT Dr. Altdorfer The tongue Anatomy, histology, innervation PowerPoint Presentation ID
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. Ascending ramus of the lateral sulcus, is located at the anterior end of the lateral sulcus (sylvian fissure), just posterior to the anterior ramus, and passes superiorly into the inferior frontal gyrus separating the pars triangularis from the pars opercularis of the frontal operculum.

TONGUE Anatomy for MBBS, NEET PG, AIIMS PG, FMGE & ALL PG YouTube
The lateral sulcus (sulcus lateralis of Sylvius), known for a long time as the Sylvian fissure, between the frontal and temporal lobes, has three branches: the anterior (ramus anterior) or horizontal ramus, the ascending (ramus ascendens) or vertical ramus and the posterior ramus (ramus posterior), separating the parietal and temporal lobes.