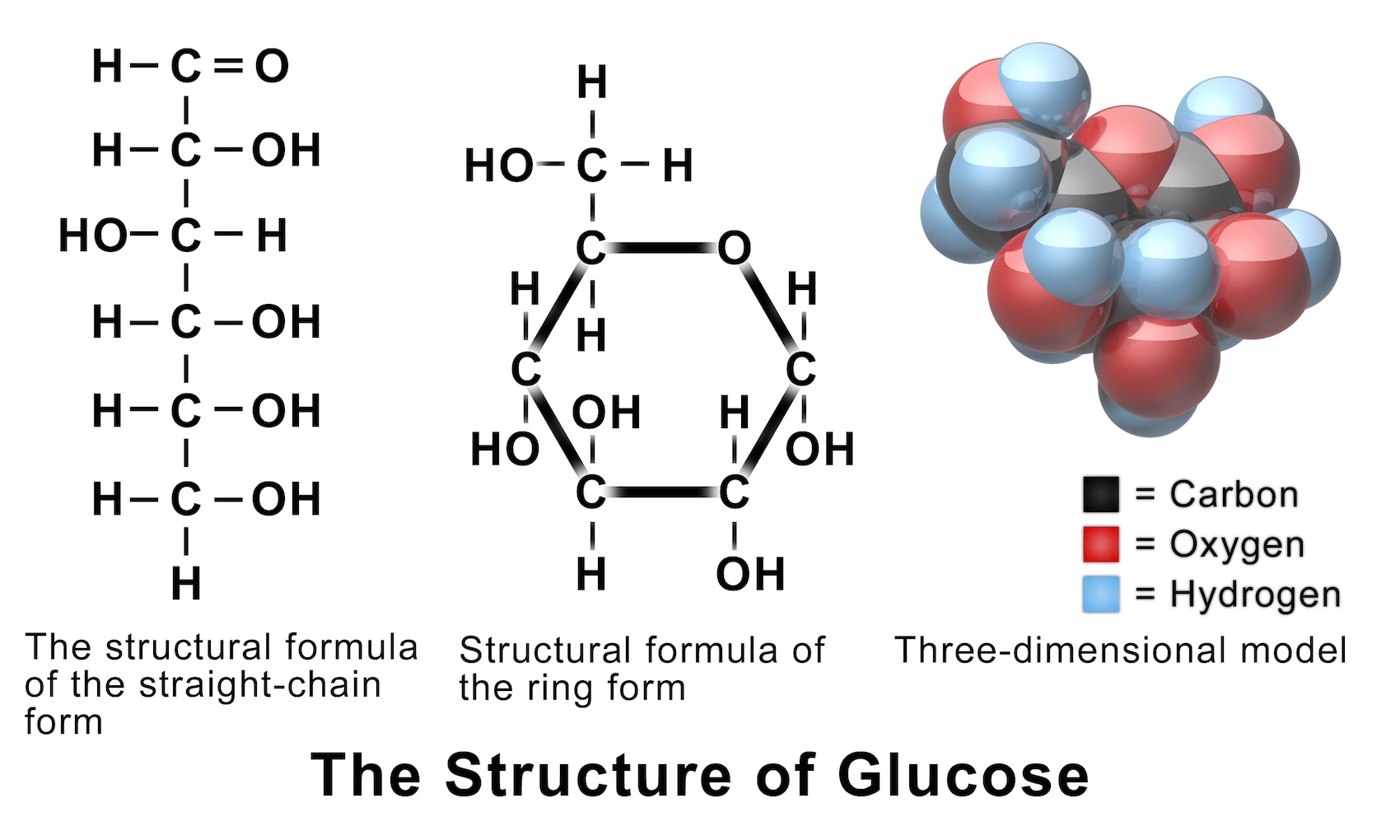
[Solved] Draw the structure of Dglucose and explain why it is much

Glucose Metabolism Diagram glucose as a hormone receptormediated
1. Although weak, multiple hydrogen bonds are important in stabilizing the three-dimensional shape of many biological molecules. (Shape determines function "functional conformation") 2. Covalent bonds are usually very stable. -cells use protein catalysts called enzymes to "break" covalent bonds e.g. hydrolysi.

Glucose (dextrose, Dglucose) molecule. Сyclic and acyclic forms
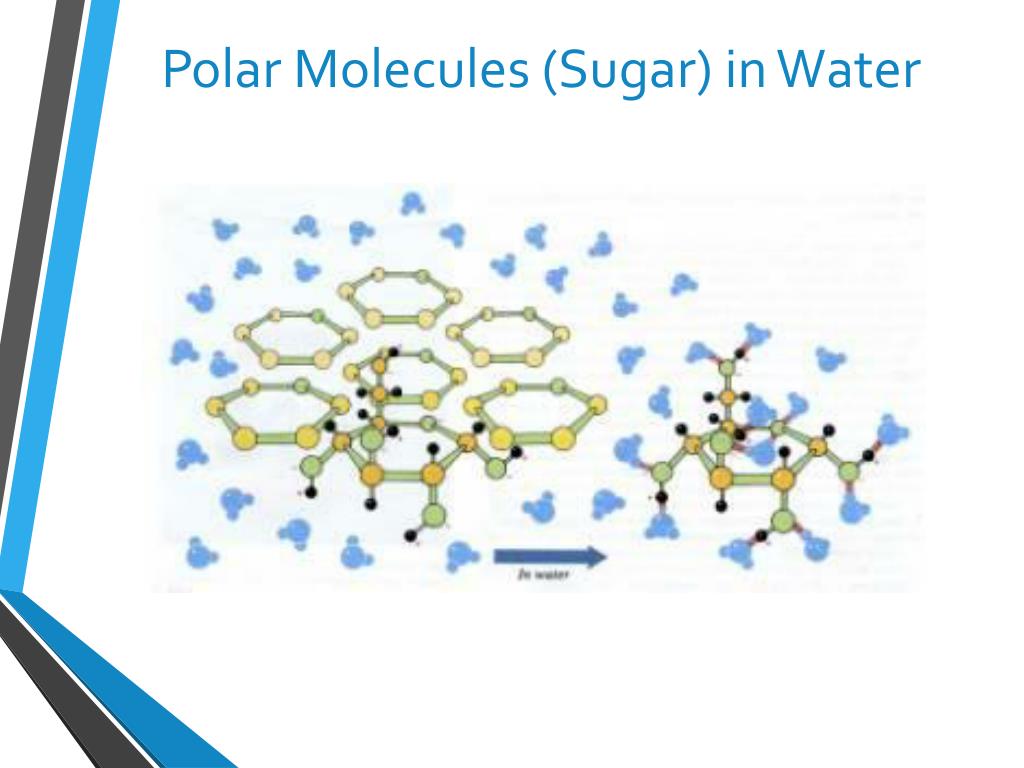
Is glucose polar? Question: Is glucose polar? Polar Molecules When two molecules are nonmetals, the bond between them can be classified as polar or nonpolar. If the electrons are shared.

Glucose (polar) Chemical Formula
Only today, enjoy all categories up to 90% off your purchase. Hurry & shop mow. Awesome prices & high quality here on Temu. New users enjoy free shipping & free return.

Sugar Polar or Nonpolar YouTube
Glucose is a key energy source for most living cells. Due to its polar nature and large size, glucose molecules cannot traverse the lipid membrane of the cell by simple diffusion. Instead, the entry of glucose molecules into the cells is effected by a large family of structurally related transport proteins known as glucose transporters.
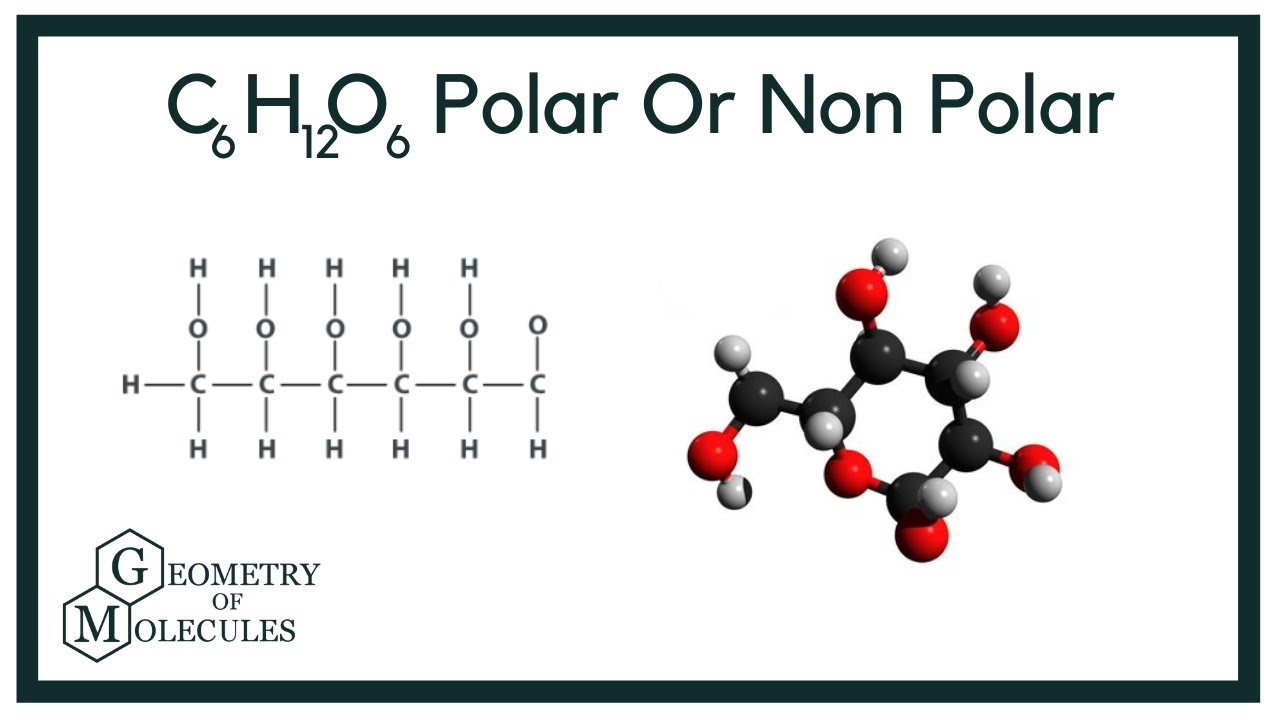
Is Glucose Polar or Nonpolar (C6H12O6) YouTube
4.4 Solubility. 4.3 Boiling Points. 4.5 Chromatography. An understanding of bond dipoles and the various types of noncovalent intermolecular forces allows us to explain, on a molecular level, many observable physical properties of organic compounds. In this section, we will concentrate on solubility, melting point, and boiling point.

PPT Atoms and Molecules PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Glucose (C6H12O6) is a polar molecule. Glucose is a six-carbon compound. It is a polyhydroxy aldehyde i.e.; it consists of five hydroxyls (OH) functional groups and an aldehyde (CHO) group at carbon number 1.

Glucose (polar) Chemical Formula
Chemical and physical properties Glucose forms white or colorless solids that are highly soluble in water and acetic acid but poorly soluble in methanol and ethanol.
PPT Solutions & Solubility PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Glucose and galactose are stereoisomers of each other: their atoms are bonded together in the same order, but they have a different 3D organization of atoms around one of their asymmetric carbons. You can see this in the diagram as a switch in the orientation of the hydroxyl (OH ) group, marked in red.This small difference is enough for enzymes to tell glucose and galactose apart, picking.

Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis The Journey to Pyruvate and
Note that they are all named using the suffix -ose, which means sugar. Carbohydrates are often named "somethingose". Figure 3.3.1 3.3. 1 These monosaccharides respect the ratio 1:2:1 mentioned above: glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ), fructose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ), galactose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ), ribose (C 5 H 10 O 5 ), deoxyribose (C 5 H 10 O 4, this one is.

Molecular Formula of Glucose BrodericksrGould
Answer link "Sugar is a highly polar molecule." Glucose, C_6H_12O_6, has 4 secondary hydroxyl groups, and 1 (exocyclic) primary hydroxyl group. Sugar is a highly polar molecule that has substantial water solubility.

Glucose C6h12o6 Is Best Described as
Trial Australia's smallest, thinnest continuous glucose monitor today for $15*. Upgrade from blood glucose monitors. One app. No transmitter. No calibration required.
[Solved] Draw the structure of Dglucose and explain why it is much
Cellulose passing through our digestive system is called dietary fiber. While the glucose-glucose bonds in cellulose cannot be broken down by human digestive enzymes, herbivores such as cows, buffalos, and horses are able to digest grass that is rich in cellulose and use it as a food source.. basic, polar, or nonpolar). The sequence and.
Is Glucose a reducing sugar?
glucose, one of a group of carbohydrates known as simple sugars ( monosaccharides ). Glucose (from Greek glykys; "sweet") has the molecular formula C 6 H 12 O 6. It is found in fruits and honey and is the major free sugar circulating in the blood of higher animals. It is the source of energy in cell function, and the regulation of its.

PPT Molecular Structure & Intermolecular Forces PowerPoint
Glucose is another example of a polar molecule because of how the oxygen atoms and hydrogen atoms are arranged. Glucose has a hexagon shape composed of 6 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms, and 6.

SolubilityPolarity YouTube
Henry Agnew (UC Davis) 5.10: Electronegativity and Bond Polarity is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Covalent bonds can be nonpolar or polar, depending on the electronegativities of the atoms involved. Covalent bonds can be broken if energy is added to a molecule.
[Solved] Why monosaccharides are more polar than disaccharides
Is glucose a polar molecule? Q: Is glucose a polar molecule? Is glucose a polar molecule? Flexi Says: The sugar glucose is a covalent compound. When sugar dissolves in water, it forms individual glucose molecules (C 6 H 12 O 6 ). You can see how this happens in the Figure here.