Resumo de Pneumonia Adquirida na Comunidade (PAC) Sanar Medicina
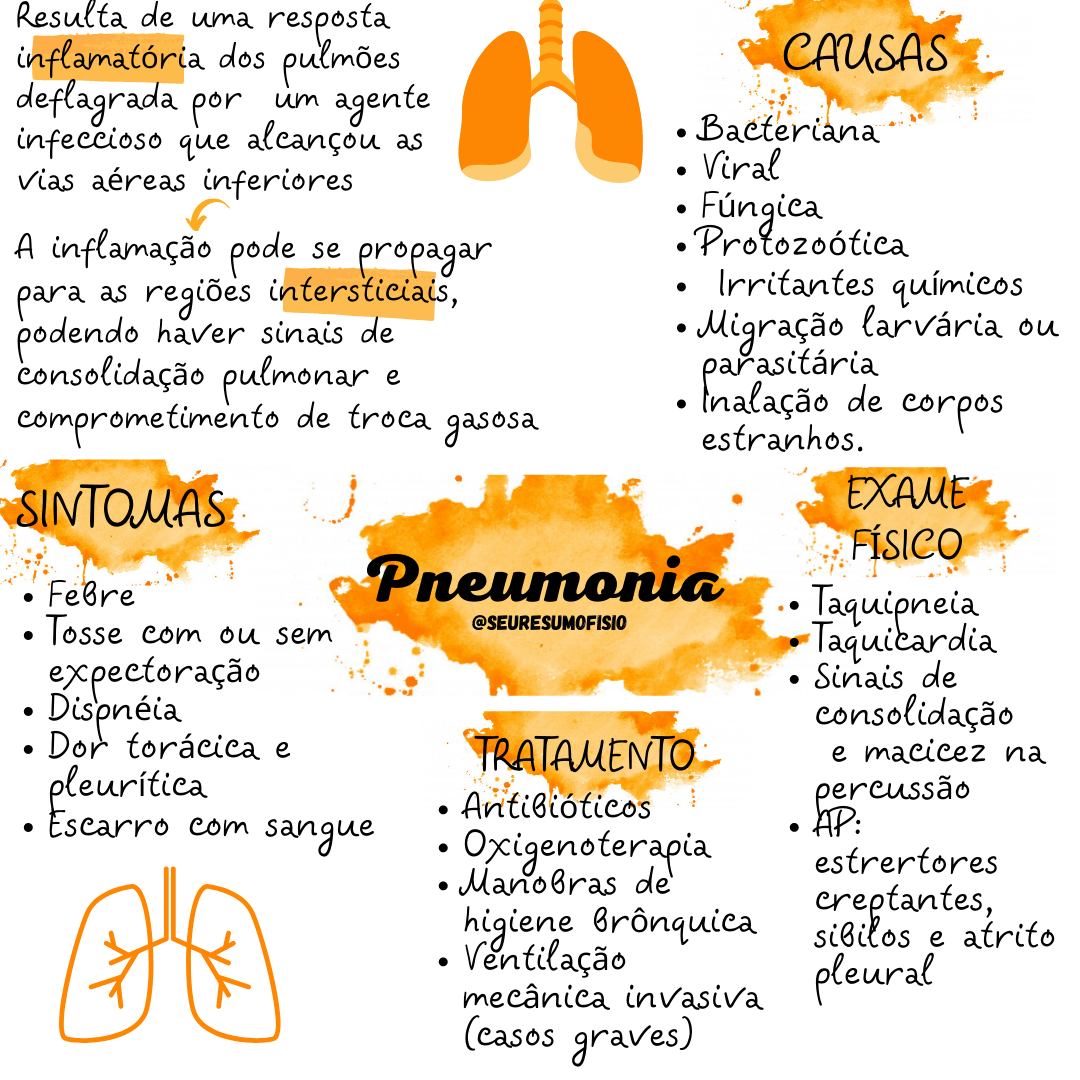
PNEUMONIA MAPA MENTAL Fisioterapia Respiratória
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the air sacs in the lungs and the surrounding tissue. It often leads to a sudden high fever, the feeling that you are very unwell, a cough and shortness of breath. Because pneumonia is usually caused by bacteria, it can generally be treated effectively with antibiotics. Vaccinations that can prevent infection by.
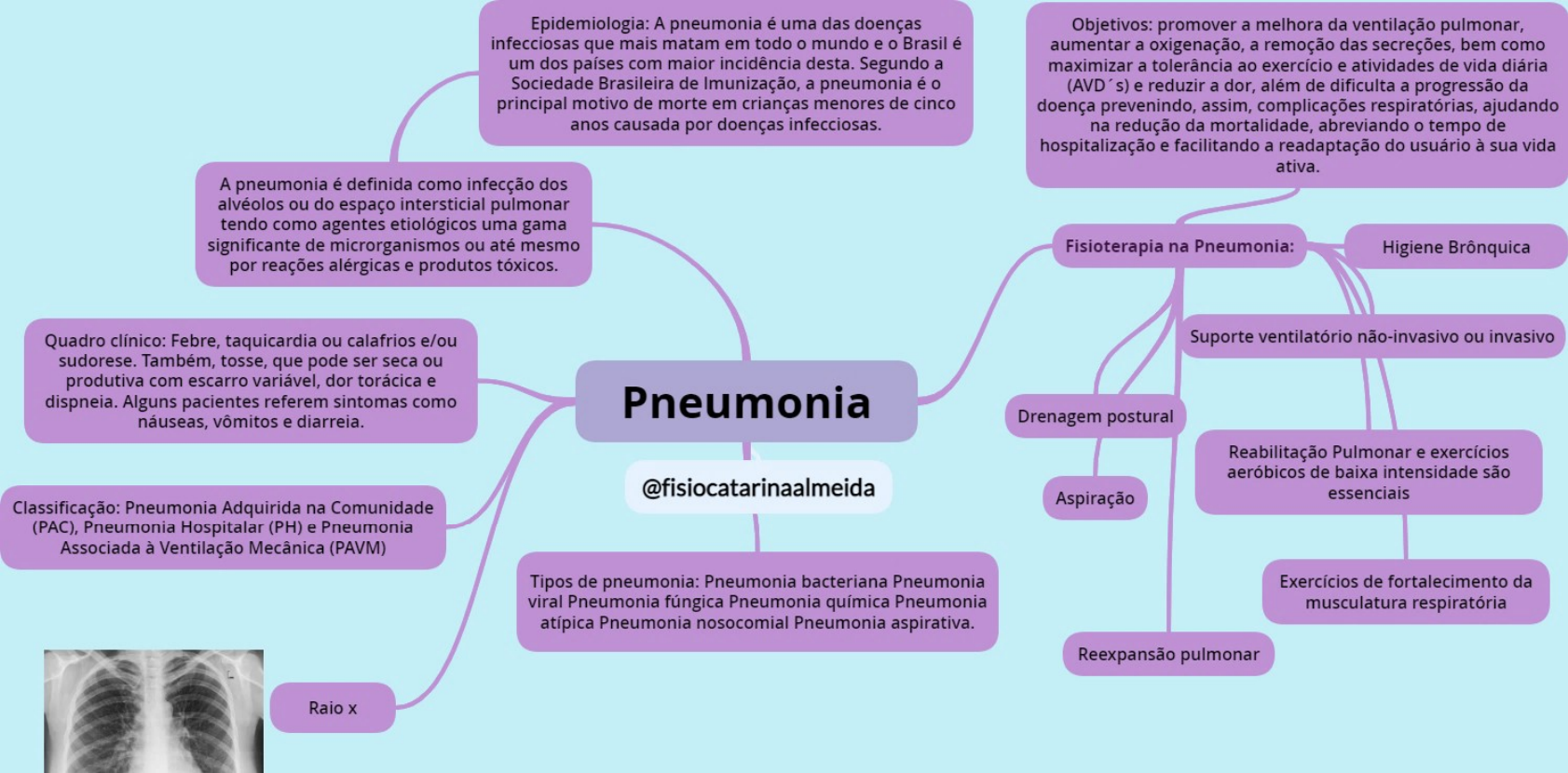
Mapa mental Pneumonia pdf Pneumonia
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a major cause of mortality and morbidity worldwide. Even when patients survive the initial insult, there is significant morbidity and mortality secondary to subsequent pulmonary edema, acute lung injury (ALI), and nosocomial pneumonia. Whereas the relationship between TBI and secondary pulmonary complications is recognized, little is known about the mechanistic.
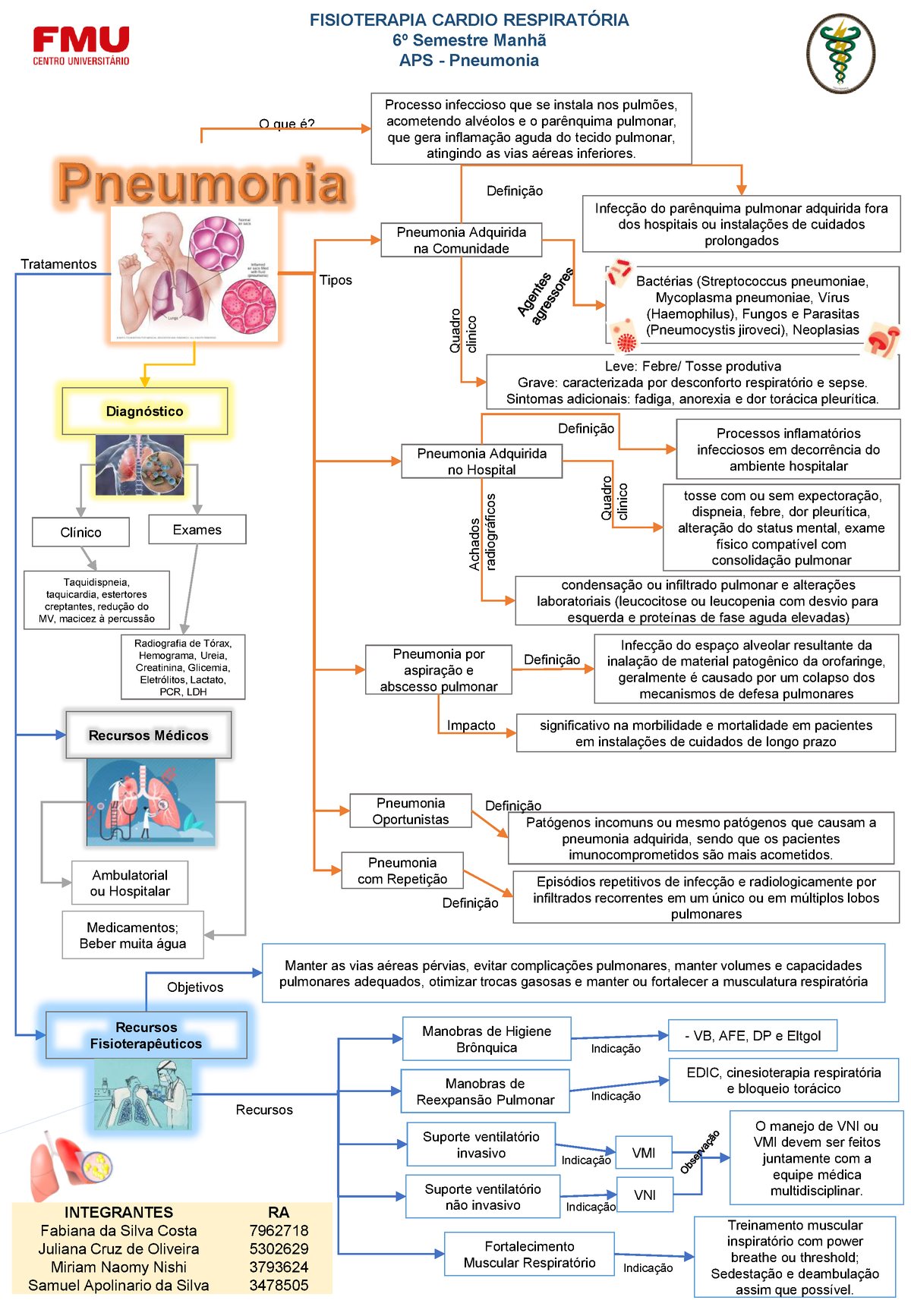
MAPA Mental Pneumonia REV01 O que é? Processo infeccioso que se
Pneumonia causes a significant public health burden in the UK in terms of morbidity and mortality. Historically, the annual incidence of community acquired pneumonia has been reported to be between 5 and 11 per 1000 adult population,1-3 estimated more recently to be between 207 and 233 per 100 000 in England.4 In 2010, influenza and pneumonia were responsible for 4.5% of all male deaths, and.
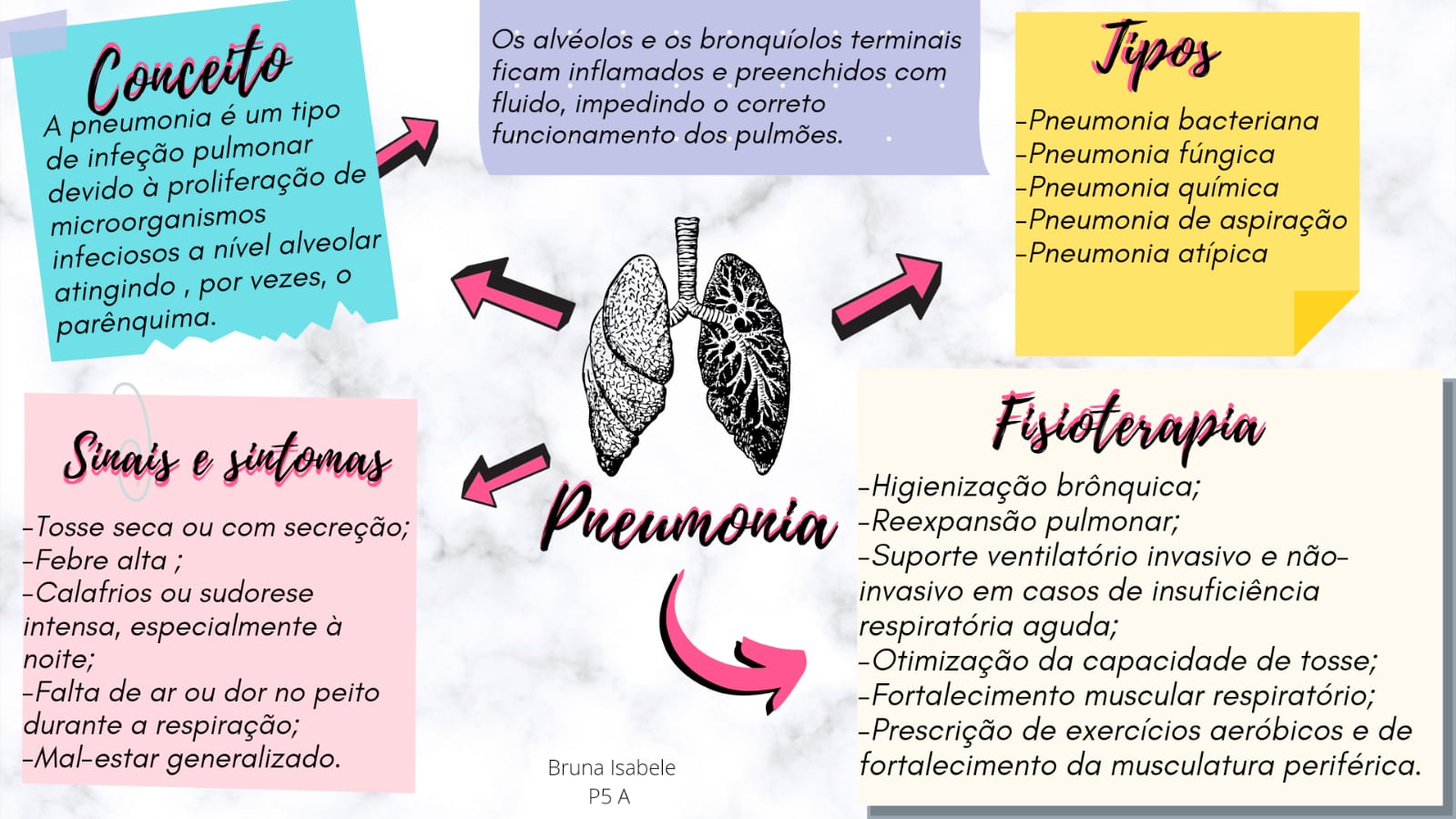
Pneumonia MAPA MENTAL Fisioterapia Pneumofuncional
This Concept Map, created with IHMC CmapTools, has information related to: Pneumonia, 69 year-old female admitted with SOB and altered mental status. Diagnosed with Pneumonia Diagnostic Tests sputum sample, accumulation of fibrous exudate, RBCs, and bacteria red hepatization & consolidation of lung parenchyma, chronic cough may bring up mucous from lungs, Adherence to alveolar macrophages.

Pneumonia em Mapa mental Fisiopatologia
The options include: Antibiotics. These medicines are used to treat bacterial pneumonia. It may take time to identify the type of bacteria causing your pneumonia and to choose the best antibiotic to treat it. If your symptoms don't improve, your doctor may recommend a different antibiotic. Cough medicine.

Pneumonia Mapa Mental
Pneumonia is acute inflammation of the lungs caused by infection. Initial diagnosis is usually based on chest x-ray and clinical findings. Causes, symptoms, treatment, preventive measures, and prognosis differ depending on whether the infection is bacterial, mycobacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic; whether it is acquired in the community or hospital; whether it occurs in a patient treated.

MAPA MENTAL SOBRE PNEUMONIA 2023 Esquemas Saúde Pública Docsity
Pneumonia is more common during the winter months. This article will focus on community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), which refers to pneumonia that develops in people in the community rather than in a hospital. About four million cases of CAP occur each year in the United States, and approximately 20 percent of people with CAP require hospitalization.
PNEUMONIA Mind Map
Diagnosis of pneumonia is based on symptoms and signs of an acute lower respiratory tract infection, and can be confirmed by a chest X-ray showing new shadowing that is not due to any other cause (such as pulmonary oedema or infarction).. (including on consent and mental capacity), and safeguarding. 1.1. Presentation with lower respiratory.

Resumo de Pneumonia Adquirida na Comunidade (PAC) Sanar Medicina
Pneumonia is an infection of the small air sacs of the lungs (alveoli) and the tissues around them. Pneumonia is one of the most common causes of death worldwide. Often, pneumonia is the final illness that causes death in people who have other serious, chronic diseases. Some types of pneumonia can be prevented by immunization.

Pneumonia Mapa Mental mapa garden
Bacteremia and Septic Shock. Lung Abscesses. Pleural Effusions, Empyema, and Pleurisy. Respiratory Failure. 5 min read. When you get pneumonia -- whether it was caused by bacteria, a virus, or a.

Mapa mental de Pneumologia doenças da pleura Sanar Medicina
Pneumonia is an umbrella term for a group of syndromes caused by a variety of organisms that result in infection of the lung parenchyma. Classification schemata have helped establish the common organisms responsible for each type of pneumonia and helped to formulate treatment guidelines for efficient management, in both inpatient and outpatient.

Pneumonia Concept Map_KPoindexter Clinical Medicine Respiratory System
Chest pain when you breathe or cough. Confusion or changes in mental awareness (in adults age 65 and older) Cough, which may produce phlegm. Fatigue. Fever, sweating and shaking chills. Lower than normal body temperature (in adults older than age 65 and people with weak immune systems) Nausea, vomiting or diarrhea.
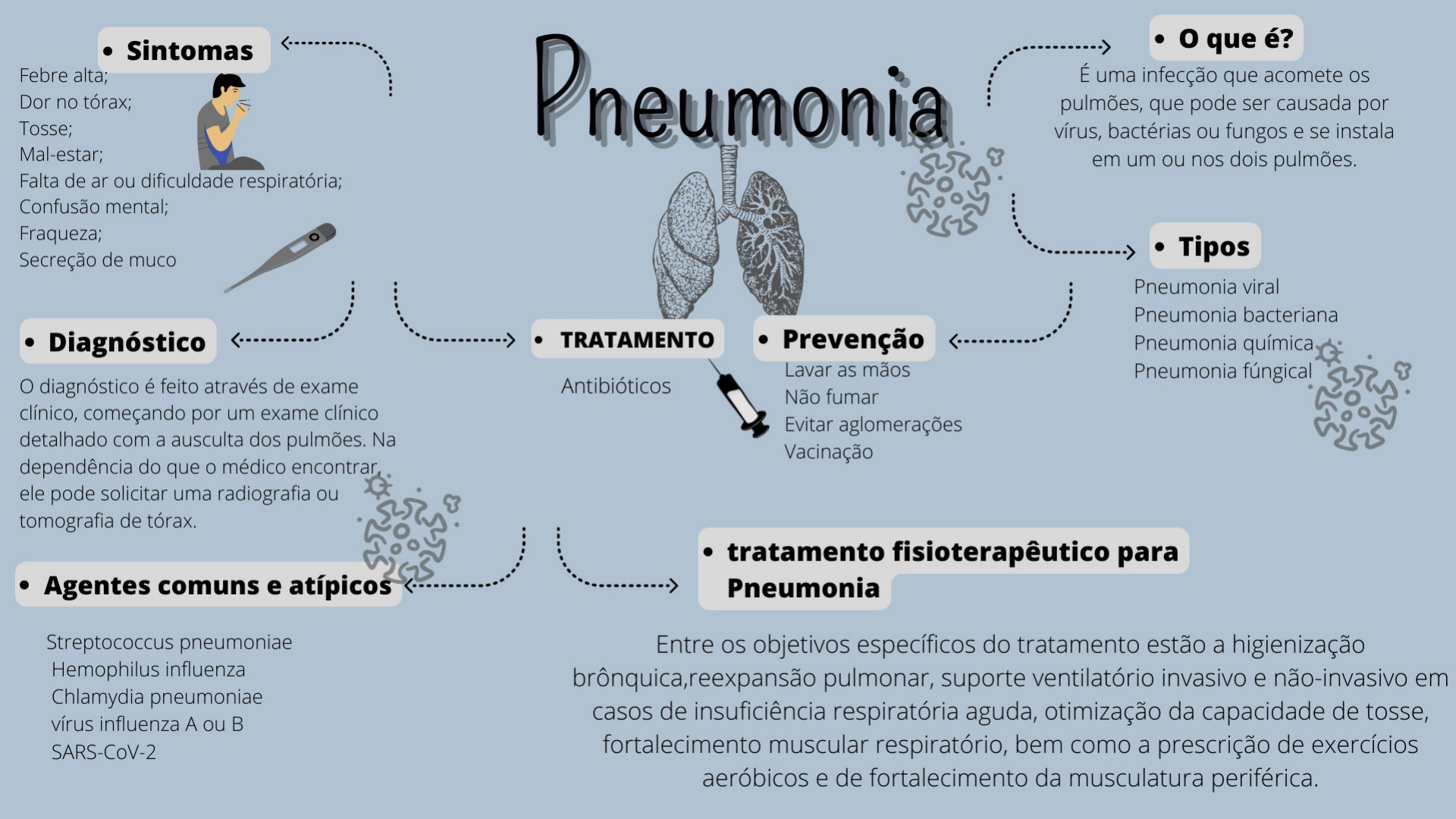
Mapa Mental Pneumonia Cardiorespiratoria
Pneumonia is inflammation and fluid in your lungs caused by a bacterial, viral or fungal infection. It makes it difficult to breathe and can cause a fever and cough with yellow, green or bloody mucus. The flu, COVID-19 and pneumococcal disease are common causes of pneumonia. Treatment depends on the cause and severity of pneumonia.
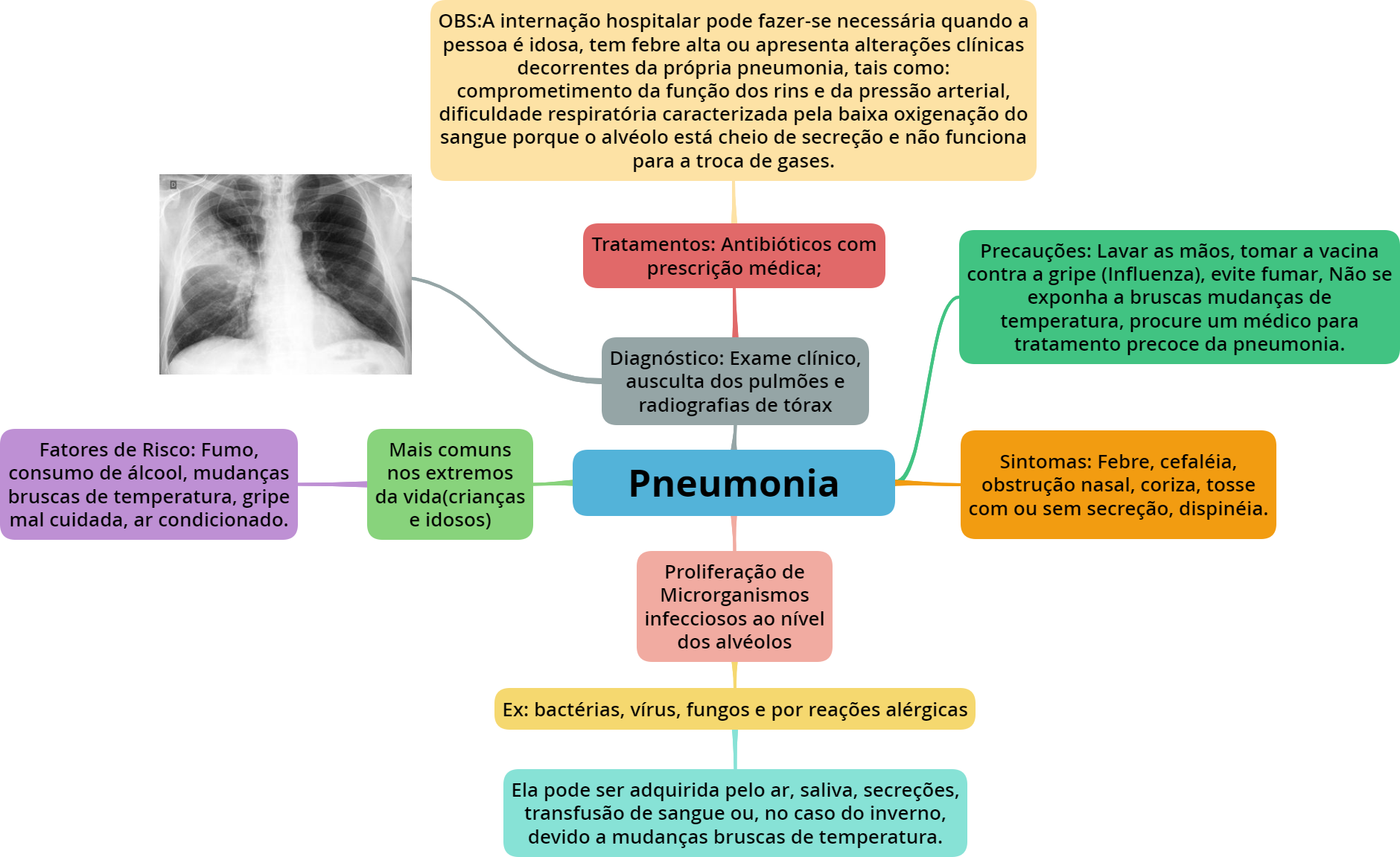
Pneumonia Mapa Mental Sistema Cardiorrespiratório
Below is an explanation of each stage. 1. Congestion. This is typically the first stage of infection that occurs after a pneumonia infection has dominated one of the lobes in your lung. The.
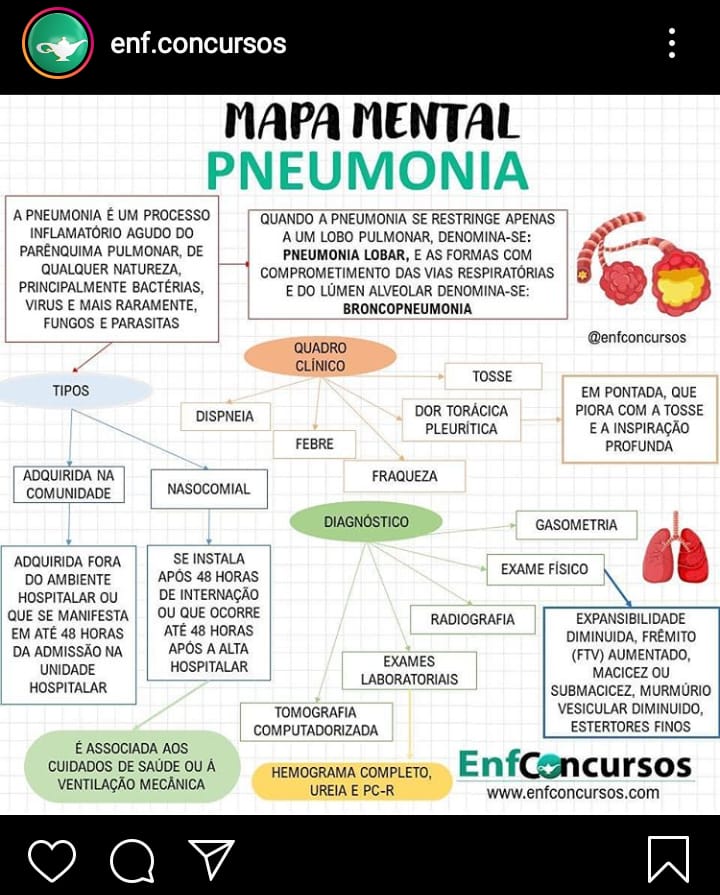
Mapa mental Pneumonia História da Enfermagem
A bout of pneumonia happens in four stages: congestion, red hepatization, grey hepatization, and resolution. The names of each stage refer to how the infection develops over time. The initial congestion stage is characterized by a wet cough, chest pain, and fever. Symptoms usually worsen in the hepatization stages, and you may have difficulty.
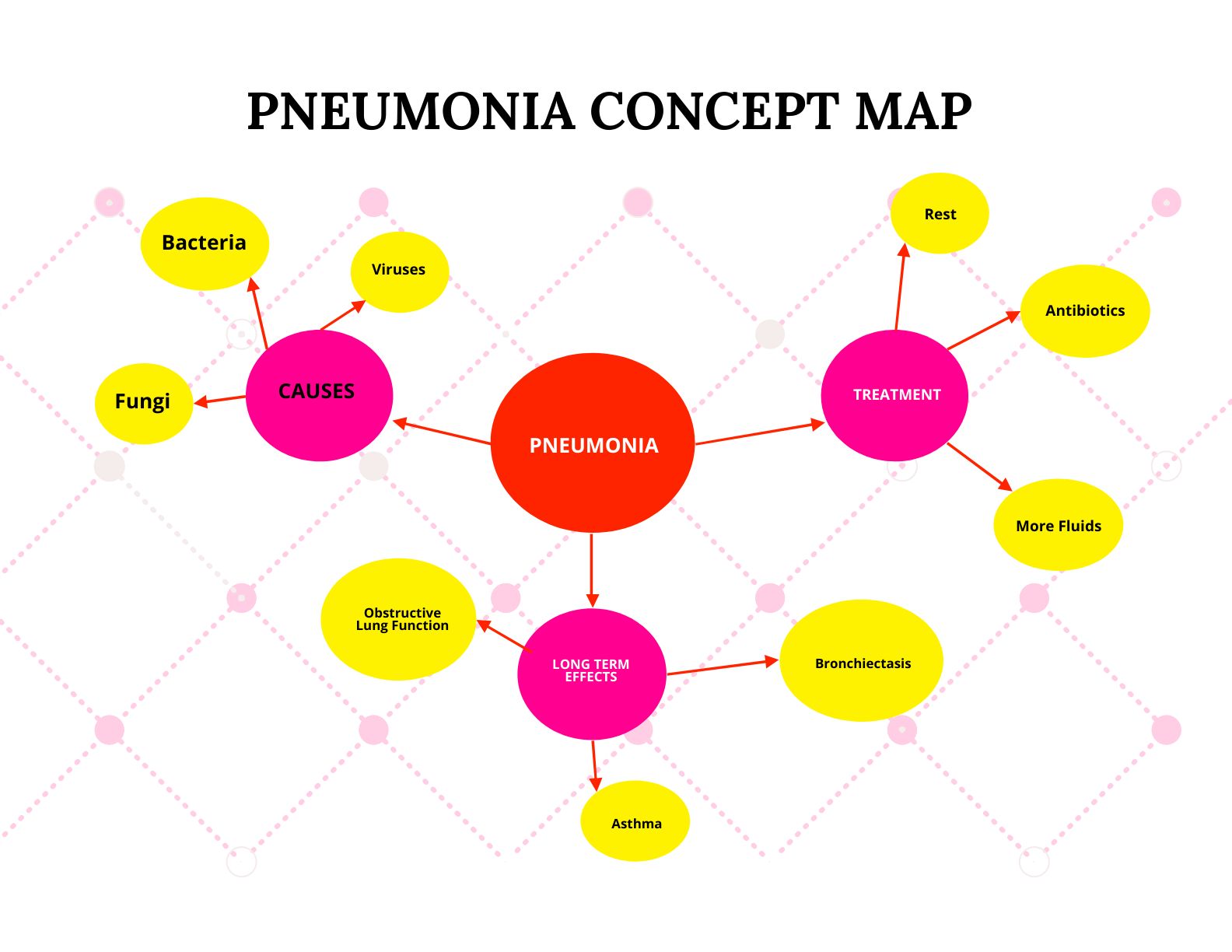
Free Pneumonia Concept Map Template Download in Word, Google Docs
24. Flu-like symptoms, decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, cough, chest pain, shortness of breath ("Hospital-acquired pneumonia",2017) 25. Gram-negative bacteria include Pseudomonas aerginosa, and E.Coli. Gram-positive organisms include Staphylococcus aeureus (Mills, Nelson, Winslow & Springer, 2009)) 26.