Epidurals Health and wellbeing Queensland Government

Cross section of the spinal cord identifying the epidural spaces... Download Scientific Diagram
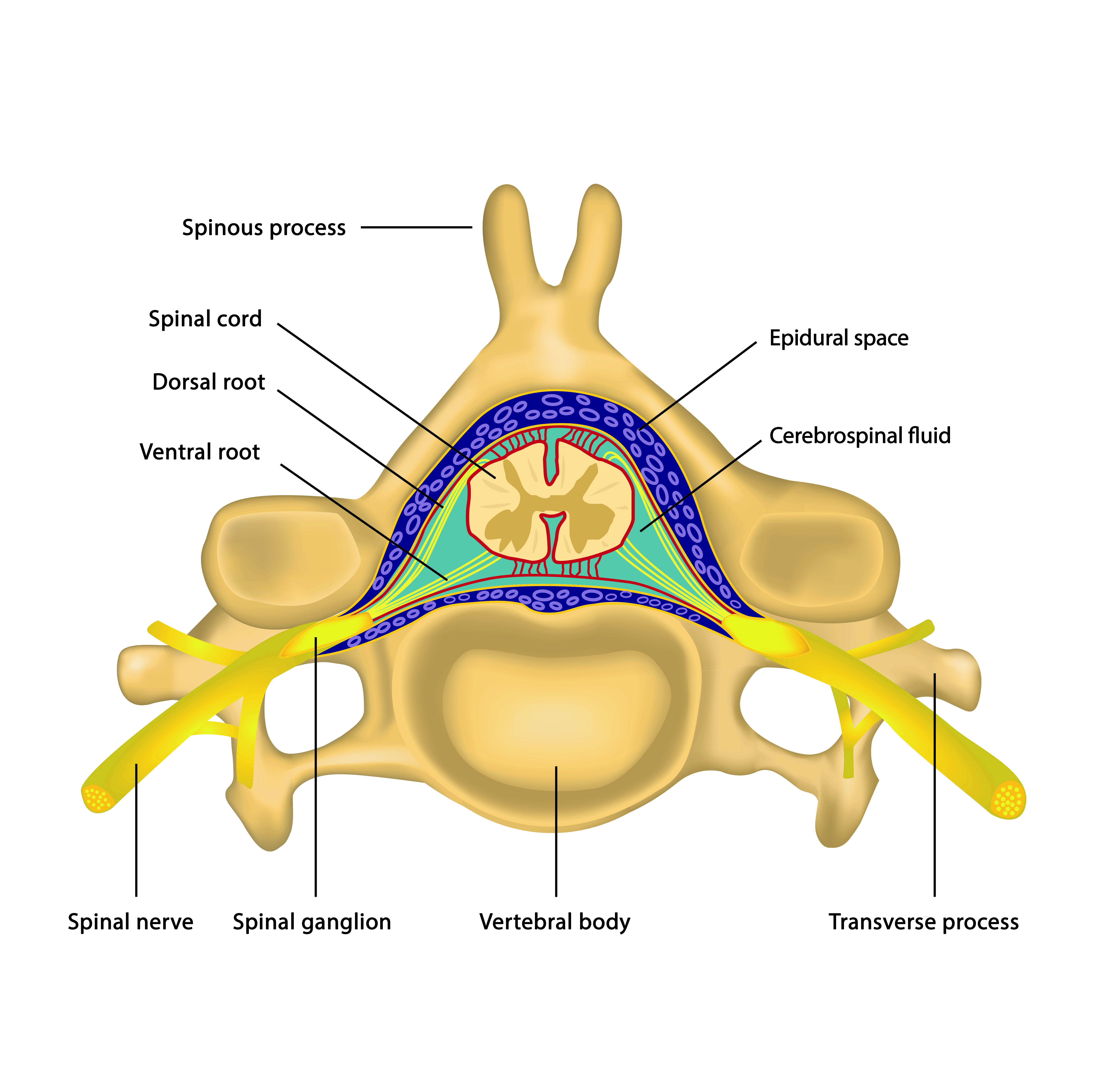
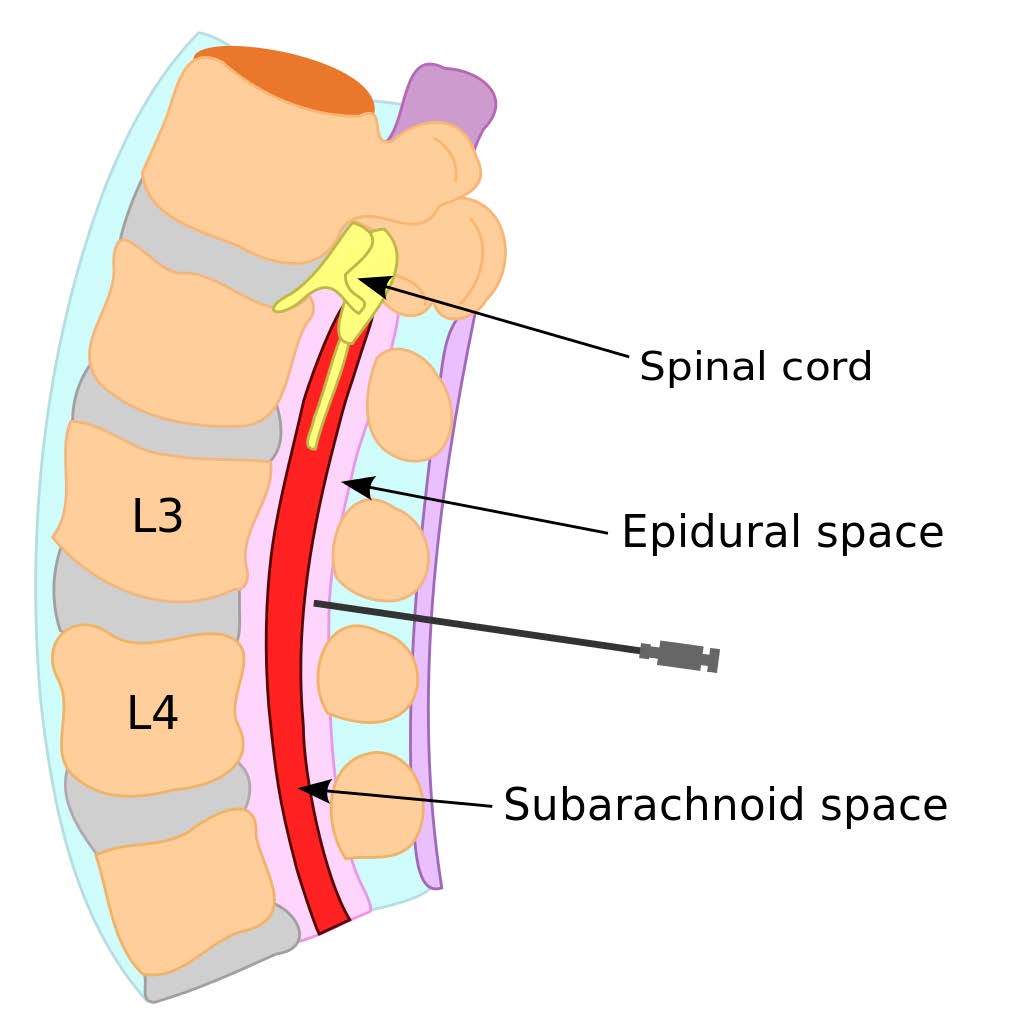
The epidural space is the area between the outermost layer of tissue and the inside surface of bone in which the spinal cord is contained, i.e., the inside surface of the spinal canal. The epidural space runs the length of the spine . The other two "spaces" are in the spinal cord itself.

Metastatic epidural spinal cord compression The Lancet Neurology
The epidural space is one of the most explored spaces of the human body. This exploration demands a good knowledge of the relevant anatomy and contents of the space. First described in 1901 (Corning JL, 1901), the epidural space is an anatomic compartment between the dural sheath and the spinal canal.

Thoracic Epidural Midline Approach Procedures CONSULT JAPAN
It contains the roots of the spinal nerves, the vertebral plexus of veins, small arteries, lymphatics and the epidural fat. This fat is loose and allows injected fluid to diffuse through it. The space projects through each intervertebral canal to lie behind the parietal pleura, whose negative pressure is transmitted to it.

Epidural Space Diagram Quizlet
Anatomy of the Epidural Space RUNE G. BLOMBERG, M.D. RUNE G. BLOMBERG, M.D. Search for other works by this author on: This Site. PubMed. Google Scholar. Author and Article Information Department of Anesthesia Central Hospital, S-601 82 Norrköping, Sweden..

where is anterior epidural or subdural space Google Search Superficial Siderosis Pinterest
Introduction The performance of any invasive medical procedure is improved by a clear understanding of the relevant anatomy. However the anatomy of the epidural space is not well described in standard medical texts nor is it clearly understood by many anaesthetists.

Vertebral Osteomyelitis Rare Spinal Infection Can Cause Severe Back Pain
In this update we revise the anatomy of the epidural space and relevant adjacent anatomy, using bespoke anatomical dissections, to enable the reader to form a 3-dimensional picture to assist their clinical practice. Sonoanatomy, common techniques for locating the epidural space, subdural anatomy and subdural block are also discussed.

How To Push During Labor What You Need To Know
This article will discuss the anatomy and function of the cranial and spinal meninges. Contents Dura mater Arachnoid mater Arachnoid granulations Subarachnoid cisterns Pia mater Spinal meninges Spinal dura mater Spinal arachnoid mater Spinal pia mater Meningeal spaces Epidural space Subdural space Subarachnoid space Clinical relations
Epidural infiltrations for treating back pain Orthopaedie Schmerztherapie
The epidural space is a tissue plane between the dura mater, covering the spinal nerve and dural sac, and the periosteum and ligaments within the vertebral canal and the intervertebral foramen (IVF). From: Braddom's Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (Sixth Edition), 2021 Neoplasm Opiate Cerebrospinal Fluid Dura Mater Local Anesthetic Inpatient
Epidurals Pain Management
Basic anatomy of the epidural space The posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL) borders the epidural space anteriorly as it overlies the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs. Laterally the medial aspect of the pedicles and the intervertebral foramina demarcate the space.
Graphical representation of the epidural space and surrounding anatomy... Download Scientific
Anatomy of the epidural space Vertebral column There are 24 individual vertebrae: seven cervical, 12 thoracic and five lumbar. The five (fused) sacral vertebrae and the coccyx (made up of 3-5 rudimentary vertebrae) are not always classed as being a part of the vertebral column. Vertebral anatomy varies according to each level.
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/epidural-space/2BSqbj86qr3ZLeoiwAHvg_spatium_epidurale_fat_02.png)
epidural space anatomy
The epidural space is important to the anaesthetist as the site for epidural block. It surrounds the spinal part of the dura and extends from the foramen magnum of the skull to the sacral hiatus. It contains the vertebral plexus of veins, small arteries, lymphatics and the epidural fat. This fat is loose and allows injected fluid to diffuse through it. The space projects through each.

Anatomy of EpiduralSubduralSubarachnoid space (from outside to inside). Download Scientific
Harold Ellis Add to Mendeley https://doi.org/10.1053/j.mpaic.2006.08.006 Get rights and content The epidural space is important to the anaesthetist as the site for epidural block. It surrounds the spinal part of the dura and extends from the foramen magnum of the skull to the sacral hiatus.

MRI of lumbar spine showing epidural space. (102) (a) Section through... Download Scientific
Definition The space outside the dura mater of the spinal cord, known as the spinal epidural space, lies between the dura and the bony vertebral canal enclosing the spinal cord. This space is crucial for administering spinal epidural anesthesia in the process of childbirth.

Easy Notes On 【Epidural Space】Learn in Just 4 Minutes! Epidural, Anatomy and physiology, Space
Basic anatomy of the epidural space The posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL) borders the epidural space anteriorly as it overlies the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs. Laterally the medial aspect of the pedicles and the intervertebral foramina demarcate the space.

Axial diagram of interlaminar lumbar epidural injection. The epidural... Download Scientific
In anatomy, the epidural space is the potential space between the dura mater and vertebrae ( spine ). [1] [2] The anatomy term "epidural space" has its origin in the Ancient Greek language; ἐπί, "on, upon" + dura mater also known as "epidural cavity", "extradural space" or "peridural space".

Administering 'topups' of epidural analgesia Nursing Times
The term " epidural space " commonly denotes the area between the dura mater, the outermost layer of the spinal meninges, and the inner surface of the vertebral canal. However, the term is also used to describe the extradural space of the cranial cavity, which typically exists as a potential space.